Figure 2:
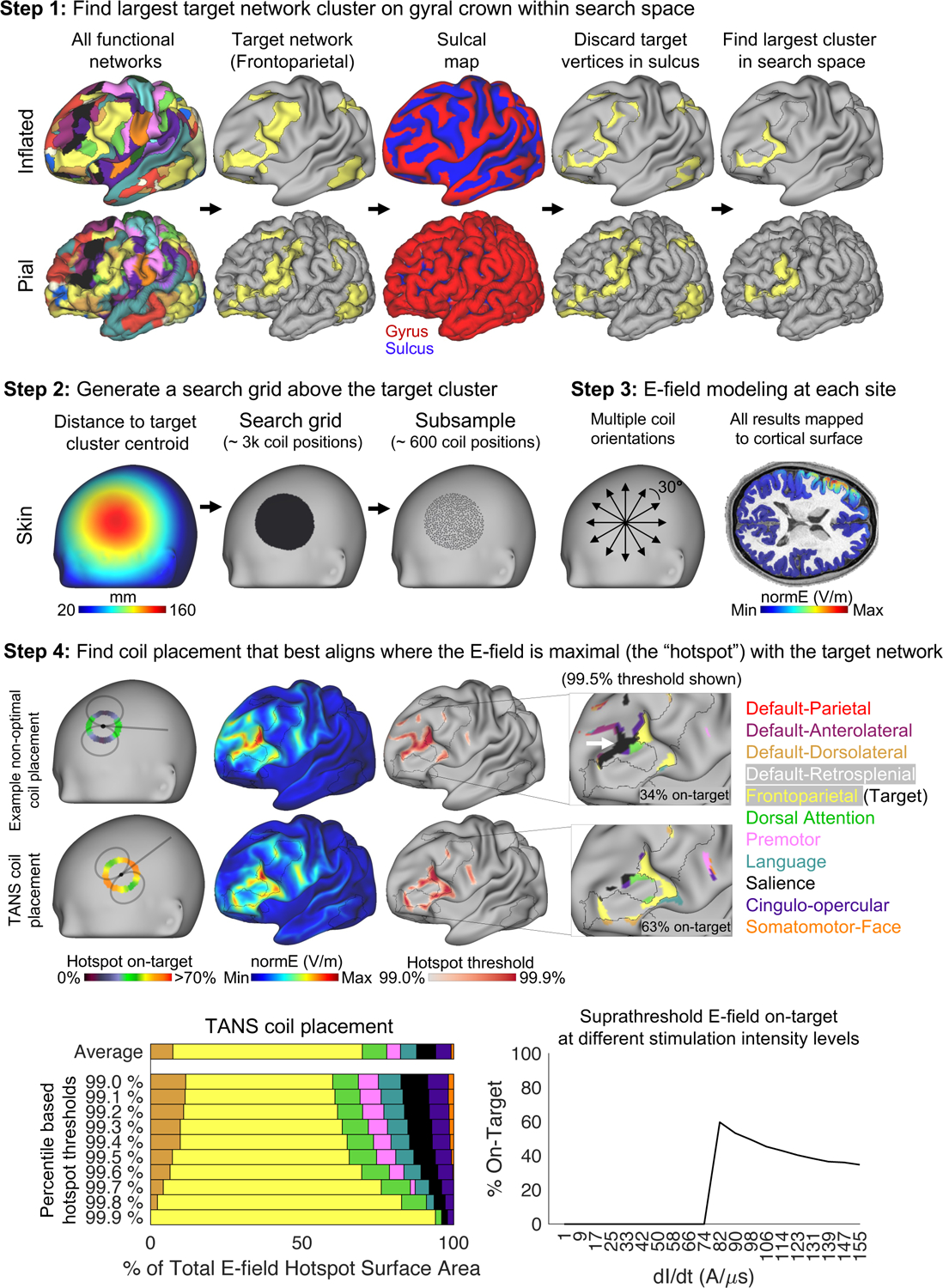
The four main steps of the Targeted Functional Network Stimulation (TANS) approach. Step 1 involves discarding target network vertices located in a sulcus in order to identify the largest piece of the target network on a gyral crown within the search space of interest (in this case, lateral prefrontal cortex). Step 2 involves creating a search grid directly above the target cluster centroid identified in Step 1. E-field modeling is performed at each point in the search grid during Step 3. Step 4 involves identifying the coil placement that best aligns where the E-field is maximal (the “hotspot”, defined for the purposes of the optimization using percentile-based thresholds) with the target functional network. The white arrow highlights off-target stimulation associated with an example non-optimal coil placement. After the optimal coil placement is found, a range of stimulation intensity levels can be modeled and the portion of the suprathreshold E-field that is on-target at each intensity level (given a specified neural activation threshold) is plotted. dl/dt = the speed of variation of the current throughout the coil.
