Figure 5.
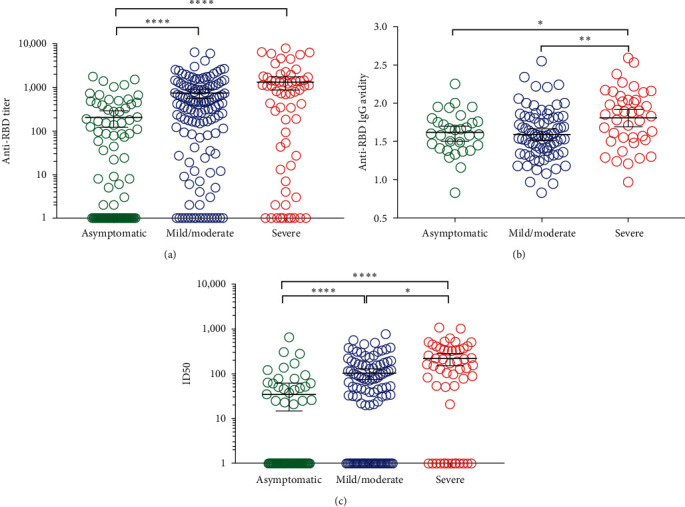
Impact of disease severity of COVID-19 recovered patients on the magnitude and quality of the anti-RBD antibody response. Sera of convalescents were stratified into three groups according to the clinical course of the disease: asymptomatic, mild/moderate, and severe. (a) Anti-RBD IgG titer was determined by RBD ELISA. Serum samples were incubated on plates coated with the RBD-mFc and were detected with an anti-human IgG mAb conjugated to horseradish peroxidase (HRP). (b) The avidity index for each sample was estimated by the incubation of sera on plates coated with the RBD-mFc, followed by the addition of NH4SCN. Bound human polyclonal antisera were detected with an anti-human mAb conjugated to HRP. The avidity index was considered as the molarity of NH4SCN reducing 50% of the bound antibodies. (c) Half-maximal inhibitory dilution (ID50) was determined by surrogate virus neutralization test (sVNT). Inhibition of binding of RBD-mFc to hACE2-hFc was assessed after preincubation of RBD-mFc with sera samples. (a) and (b) The p values were calculated by the nonparametric Kruskal–Wallis test, where ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 and ∗p < 0.05, adjusted for multiple comparisons by Dunn's test. (c) The p values were calculated by the one way ANOVA test, where ∗p < 0.05 and ∗∗p < 0.005, adjusted for multiple comparisons by Holm–Sidak's test.
