Figure 1.
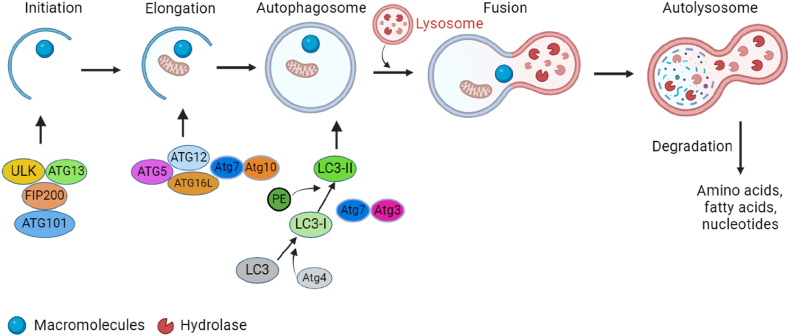
The five stages of autophagy are initiation, elongation and autophagosome formation, fusion, and autolysosome formation. Targeting macromolecules to double-membrane vesicles known as autophagosomes leads to autolysosome formation by lysosome fusion. The Unc-51-like autophagy-activating kinases 1 (ULK1) complex, which includes ULK, autophagy-related gene (ATG) protein 13, FIP200, and ATG101, triggers autophagy. Two ubiquitin-like conjugation systems, such as the ATG12 and microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B-light chain 3 (LC3) systems, are involved in the elongation and maturation of autophagosomes. An autolysosome is formed by the fusion of the autophagosome with the lysosome. This autolysosome breaks down macromolecules into amino acids, fatty acids, and nucleotides.24 ATG: Autophagy-related gene; FIP200: FAK family-interacting protein of 200 kDa; LC3: Light chain 3; PE: Phosphatidylethanolamine; ULK: Unc-51-like autophagy-activating kinase; ULK1: Unc-51-like autophagy-activating kinase 1.