Abstract
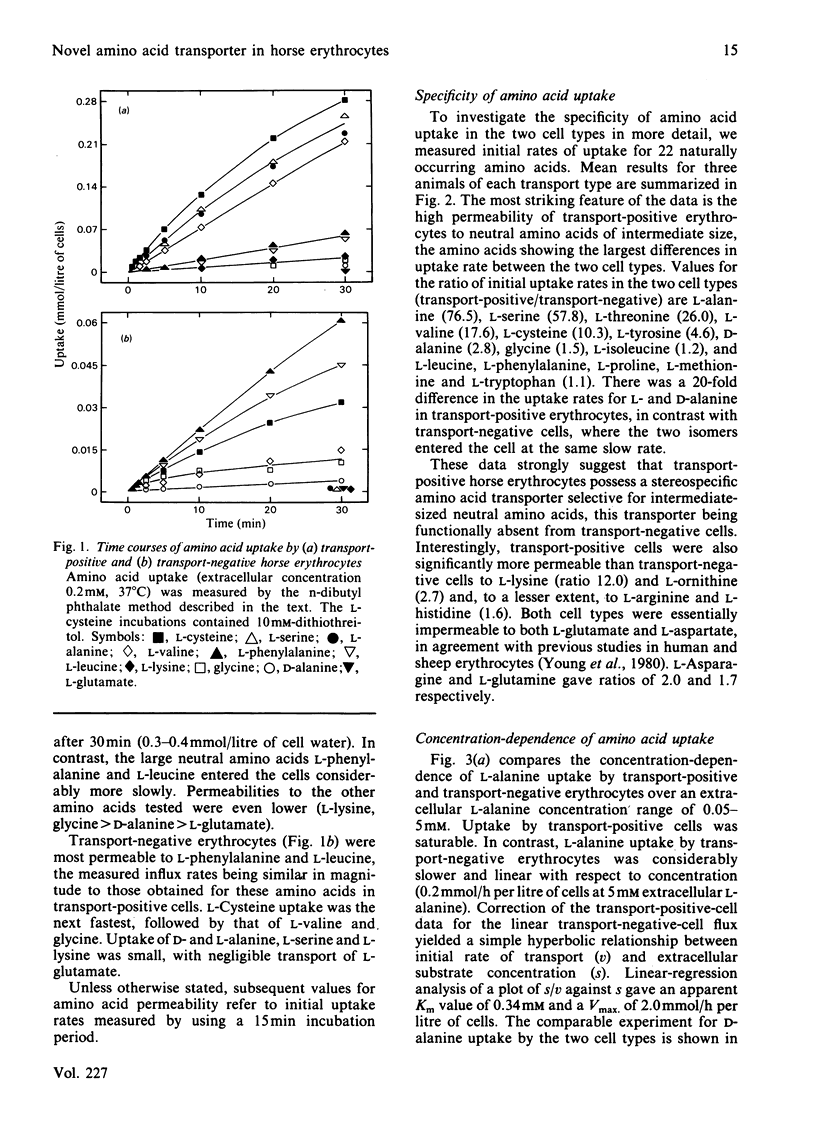
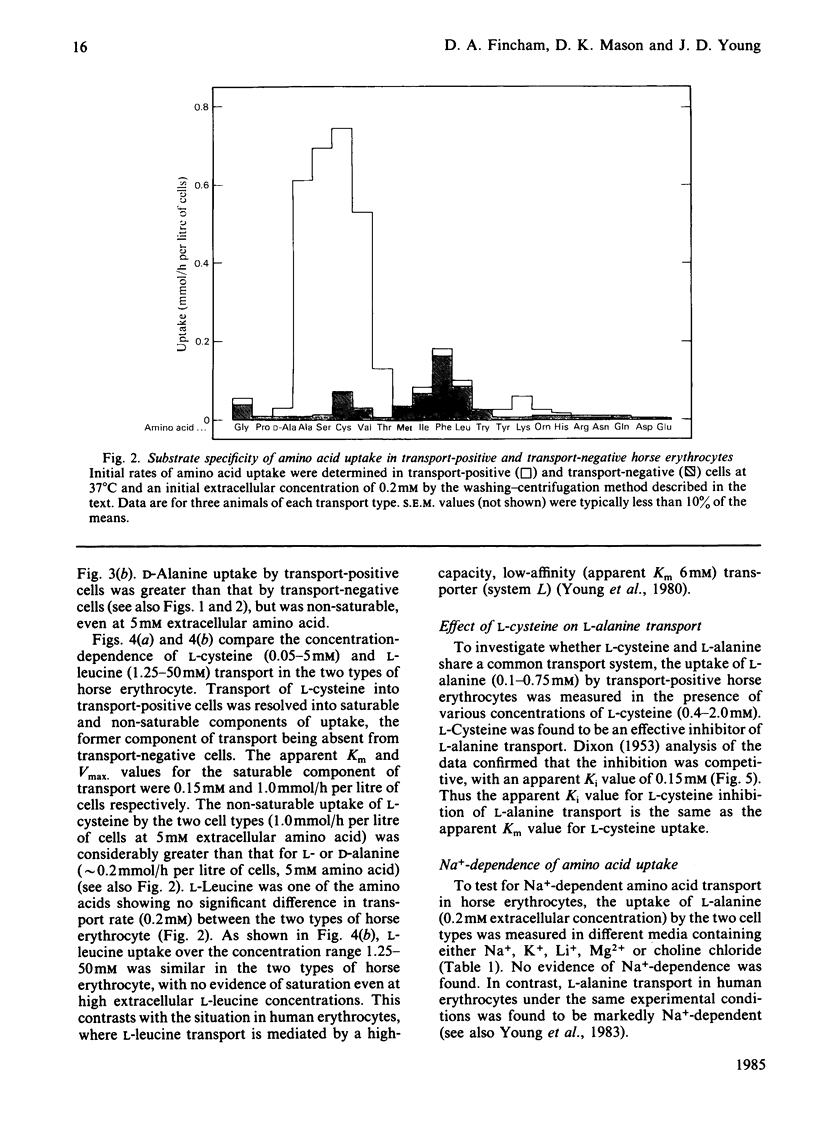
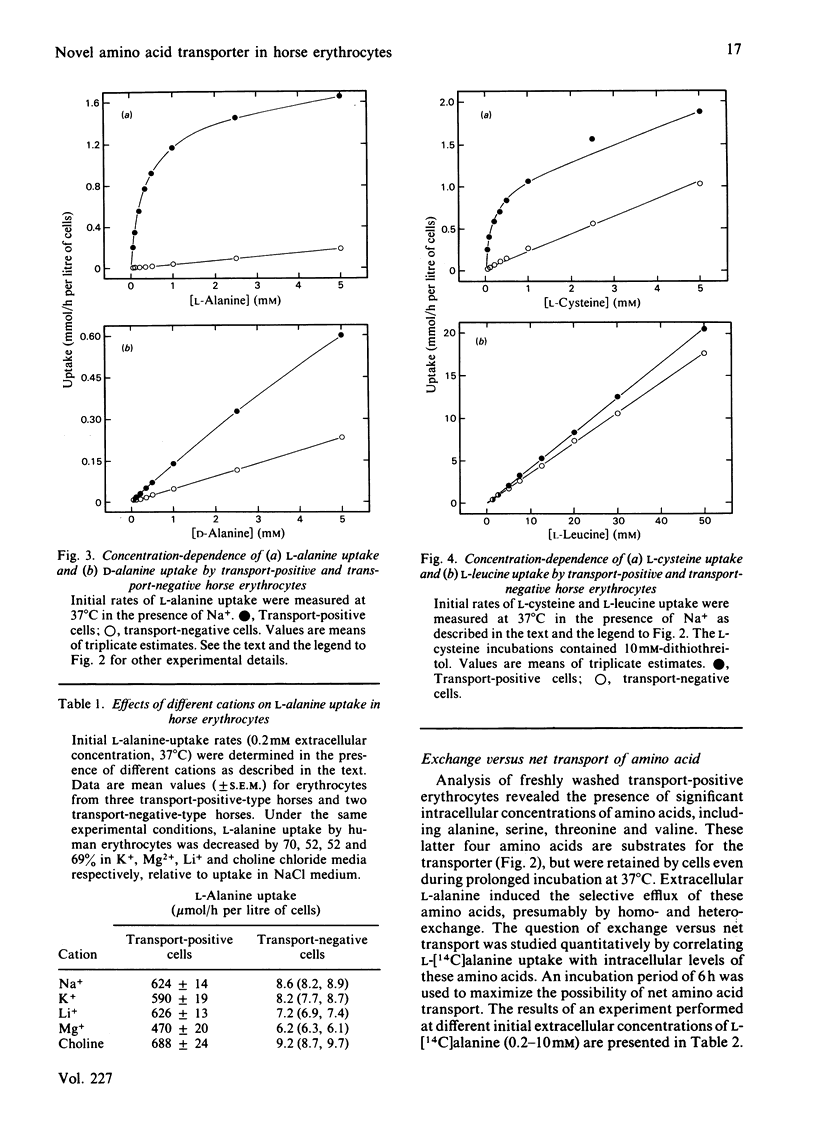
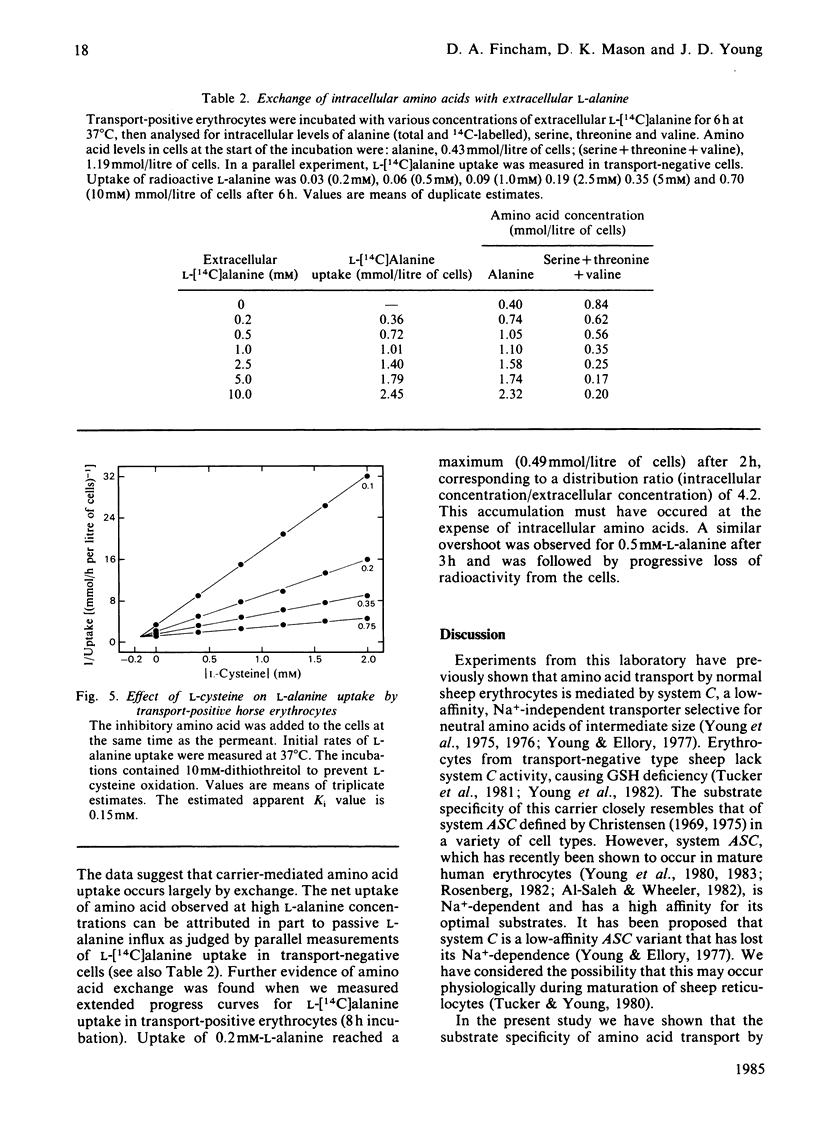
Horse erythrocytes are polymorphic with respect to L-alanine permeability. The present investigation compared the specificity, kinetics and cation-dependence of erythrocyte amino acid transport in two groups of thoroughbred horses, those with erythrocyte L-alanine permeabilities in the range 5-15 mumol/h per litre of cells (0.2 mM extracellular L-alanine, 37 degrees C) (transport-negative type) and those with L-alanine permeabilities in the range 450-700 mumol/h per litre of cells (transport-positive type). Transport-positive cells are shown to possess a novel high-affinity, stereospecific, Na+-independent transporter selective for neutral amino acids of intermediate size. This carrier system (provisional designation asc) operates preferentially in an exchange mode and is functionally absent from erythrocytes of transport-negative-type horses.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al-Saleh E. A., Wheeler K. P. Transport of neutral amino acids by human erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jan 22;684(2):157–171. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90001-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannai S., Christensen H. N., Vadgama J. V., Ellory J. C., Englesberg E., Guidotti G. G., Gazzola G. C., Kilberg M. S., Lajtha A., Sacktor B. Amino acid transport systems. 1984 Sep 27-Oct 3Nature. 311(5984):308–308. doi: 10.1038/311308b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen H. N. Exploiting amino acid structure to learn about membrane transport. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1979;49:41–101. doi: 10.1002/9780470122945.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen H. N., Handlogten M. E., Thomas E. L. Na plus-facilitated reactions of neutral amino acids with a cationic amino acid transport system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jul;63(3):948–955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.3.948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen H. N. Some special kinetic problems of transport. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1969;32:1–20. doi: 10.1002/9780470122778.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON M. The determination of enzyme inhibitor constants. Biochem J. 1953 Aug;55(1):170–171. doi: 10.1042/bj0550170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellory J. C., Tucker E. M., Deverson E. V. The identification of ornithine and lysine at high concentrations in the red cells of sheep with an inherited deficiency of glutathione. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Oct 25;279(3):481–483. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90169-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. Na-independent and Na-dependent transport of neutral amino acids in the human red blood cell. Acta Physiol Scand. 1982 Dec;116(4):321–330. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1982.tb07149.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. L., Christensen H. N. Indications of spatial relations among structures recognizing amino acids and Na+ at a transport receptor site. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jul 27;40(2):277–283. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)91006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. L., Christensen H. N. Nature of the cosubstrate action of Na+ and neutral amino acids in a transport system. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1682–1688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. L., Shao T. C., Christensen H. N. Structural selectivity in interaction of neutral amino acids and alkali metal ions with a cationic amino acid transport system. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1677–1681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker E. M. A shortened life span of sheep red cells with a glutathione deficiency. Res Vet Sci. 1974 Jan;16(1):19–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker E. M., Young J. D. Biochemical changes during reticulocyte maturation in culture. A comparison of genetically different sheep erythrocytes. Biochem J. 1980 Oct 15;192(1):33–39. doi: 10.1042/bj1920033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker E. M., Young J. D., Crowley C. Red cell glutathione deficiency: clinical and biochemical investigations using sheep as an experimental model system. Br J Haematol. 1981 Jul;48(3):403–415. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1981.tb02732.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Ellory J. C. Substrate specificity of amino acid transport in sheep erythrocytes. Biochem J. 1977 Jan 15;162(1):33–38. doi: 10.1042/bj1620033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Ellory J. C., Tucker E. M. Amino acid transport defect in glutathione-deficient sheep erythrocytes. Nature. 1975 Mar 13;254(5496):156–157. doi: 10.1038/254156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Ellory J. C., Tucker E. M. Amino acid transport in normal and glutathione-deficient sheep erythrocytes. Biochem J. 1976 Jan 15;154(1):43–48. doi: 10.1042/bj1540043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Jones S. E., Ellory J. C. Amino acid transport in human and in sheep erythrocytes. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1980 Sep 26;209(1176):355–375. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1980.0100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Tucker E. M., Kilgour L. Genetic control of amino acid transport in sheep erythrocytes. Biochem Genet. 1982 Aug;20(7-8):723–731. doi: 10.1007/BF00483969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Wolowyk M. W., Jones S. M., Ellory J. C. Red-cell amino acid transport. Evidence for the presence of system ASC in mature human red blood cells. Biochem J. 1983 Nov 15;216(2):349–357. doi: 10.1042/bj2160349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


