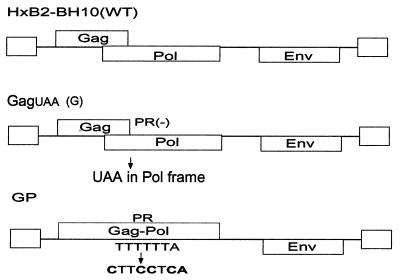
FIG. 4.
Schematic representation of WT control and G and GP plasmid DNA used in cotransfections for the production of viral particles containing mutations in cleavage sites in either Gag or Gag-Pol. WT HXB2-BH10 was used for the construction of both the GagUAA (G) and the GP clones. The G plasmid was constructed by using PCR stitch mutagenesis in order to introduce a stop codon within the frame of the Pol protein. The Gag-Pol expression plasmid (GP) has been previously described (37). The frameshift mutation introduced here allows continuous expression of Gag-Pol and bypasses the Gag termination codon. The DNA regions containing mutations within the primary cleavage site (p2/NC) or in primary and tertiary cleavage sites (p2/NC and CA/p2) were removed from CA2 or CA6 mutants and cloned into the G and GP plasmids via SpeI and ApaI restriction enzyme sites, respectively. The resultant mutants were termed GCA2, GCA6, GPCA2, and GPCA6 (see also Table 2). The G plasmid was then cotransfected with either GPCA2 alone or in combination with GPCA6 while the GP plasmid was cotransfected with either GCA2 alone or in combination with GCA6 in 293T cells.