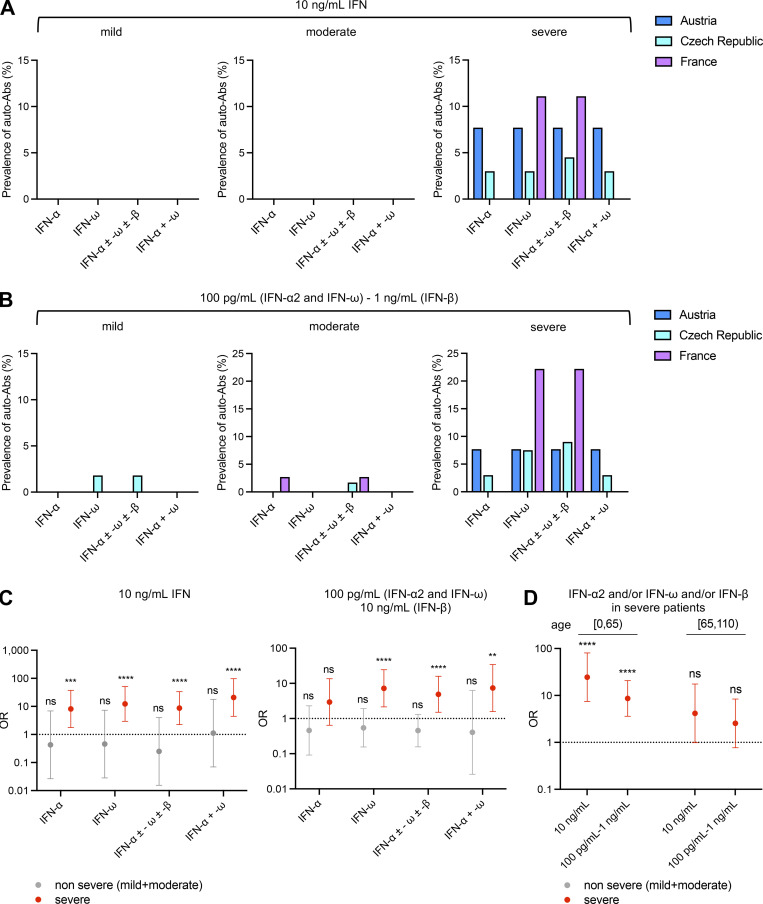
Figure 2.
Comparison of the proportions of individuals positive for auto-Abs neutralizing type I IFNs in the different TBE cohorts and estimation of the risk of severe TBE in auto-Ab-positive individuals relative to the general population. (A) Comparison of auto-Ab prevalence in TBE patients from the Austrian, Czech, and French cohorts (considering auto-Abs neutralizing 10 ng/ml IFN). IFN-α, auto-Abs neutralizing IFN-α2 (regardless of their effects on other IFNs); IFN-ω, auto-Abs neutralizing IFN-ω (regardless of their effects on other IFNs); IFN-α ± ω ± β, auto-Abs neutralizing IFN-α2 and/or IFN-ω and/or IFN-β; IFN-α + ω, auto-Abs neutralizing both IFN-α2 and IFN-ω. (B) Comparison of auto-Ab prevalence in TBE patients from the Austrian, Czech, and French cohorts (considering auto-Abs neutralizing 100 pg/ml [IFN-α2 and IFN-ω] or 1 ng/ml [IFN-β]). IFN-α, auto-Abs neutralizing IFN-α2 (regardless of their effects on other IFNs); IFN-ω, auto-Abs neutralizing IFN-ω (regardless of their effects on other IFNs); IFN-α ± ω ± β, auto-Abs neutralizing IFN-α2 and/or IFN-ω and/or IFN-β; IFN-α + ω, auto-Abs neutralizing both IFN-α2 and IFN-ω. (C) OR for the presence of auto-Abs in individuals with non-severe (gray) or severe (red) TBE relative to the general population, with adjustment for age and sex by logistic regression. The horizontal bars indicate the upper and lower limits of the 95% CI. IFN-α, auto-Abs neutralizing IFN-α2 (regardless of their effects on other IFNs); IFN-ω, auto-Abs neutralizing IFN-ω (regardless of their effects on other IFNs); IFN-α ± ω ± β, auto-Abs neutralizing IFN-α2 and/or IFN-ω and/or IFN-β; IFN-α + ω, auto-Abs neutralizing both IFN-α2 and IFN-ω. (D) OR for the presence of auto-Abs in individuals with severe TBE relative to the general population by age group, with adjustment for sex by logistic regression. ORs were calculated separately for patients with severe TBE aged ≤65 and >65 years. The horizontal bars indicate the upper and lower limits of the 95% CI. IFN-α, auto-Abs neutralizing IFN-α2 (regardless of their effects on other IFNs); IFN-ω, auto-Abs neutralizing IFN-ω (regardless of their effects on other IFNs); IFN-α ± ω ± β, auto-Abs neutralizing IFN-α2 and/or IFN-ω and/or IFN-β; IFN-α + ω, auto-Abs neutralizing both IFN-α2 and IFN-ω. [0,65): individuals aged 0–65 years old; [65,110): individuals aged 65–110 years old; ns: non-significant; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.