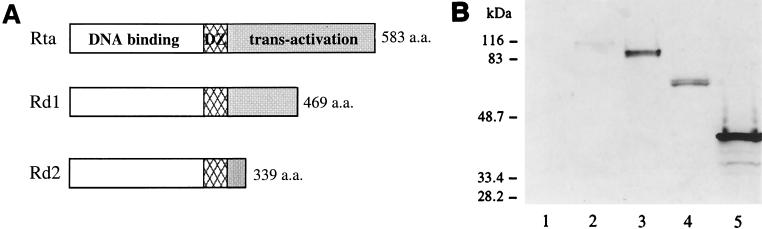
FIG. 1.
Construction and expression of wild-type and mutant Rta proteins. (A) The structures of the wild-type and mutant Rta proteins are shown, with the open boxes representing the DNA binding domains, the hatched boxes representing the dimerization domains (DZ), and the shaded boxes representing the activation domains. The size of each protein is indicated at the right. (B) Wild-type and mutant Rta proteins are expressed in 293T cells. The coding sequences of Rta, Rd1, and Rd2 were individualy cloned into pCMVFLAG. The cells were transfected with the empty vector, pCMVFLAG (lane 1), pCMVFLAG/Rta/KSHV (lane 2), pCMVFLAG/Rta (lane 3), pCMVFLAG/Rd1 (lane 4), or pCMVFLAG /Rd2 (lane 5). Ten percent of the total cell lysates was loaded onto a 10% denaturing polyacrylamide gel. Western blot analysis was carried out using the monoclonal antibody against the FLAG epitope. The masses of individual proteins in the molecular weight standard are indicated at the left.