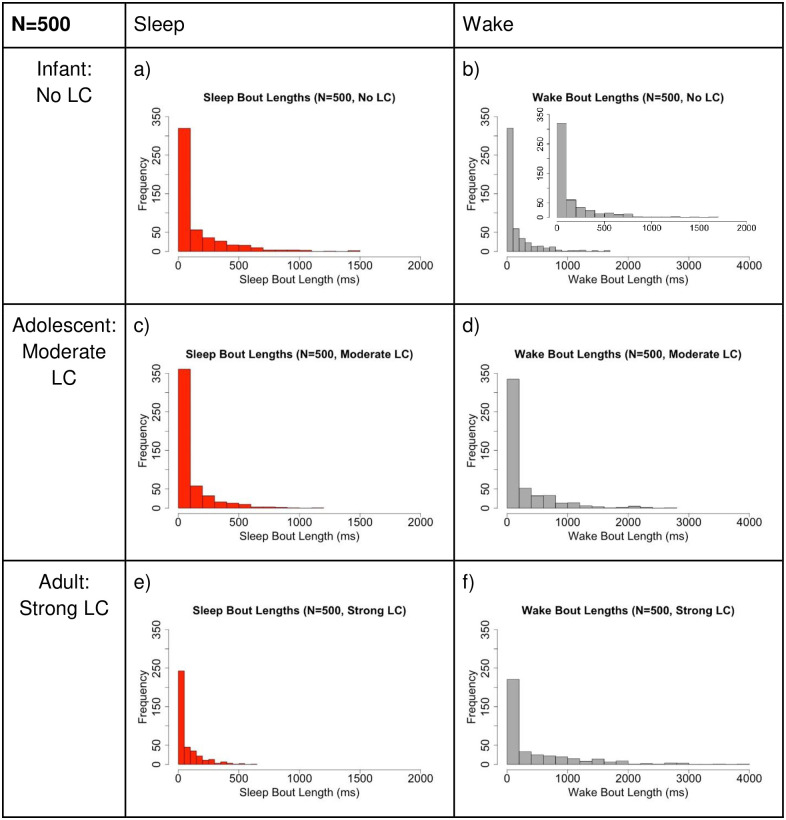
Fig 15. Larger network comparison of the distribution of sleep and wake bout lengths.
Comparison of the distribution of sleep vs. wake bout lengths for different levels of LC connectivity for N = 500. Note the y-axis is consistent for all cases, but the x-axis differs between sleep and wake. Left (SA case): Increasing the LC strength does not change the average sleep bout length much, and the distribution remains exponential. Right: (WA case): Wake bout durations lengthen on average as LC strength increases, and the shape of the distribution of bout lengths differs noticeably from exponential in the case of no LC interaction. In panel b), the inset graph shows the same data, but plotted with the same x-axis as the SA case. This shows that with no LC interaction, the WA and SA distributions are nearly identical. Larger x-axis is used for WA plots to show the increase in observed bout lengths as LC-WA interaction is increased.