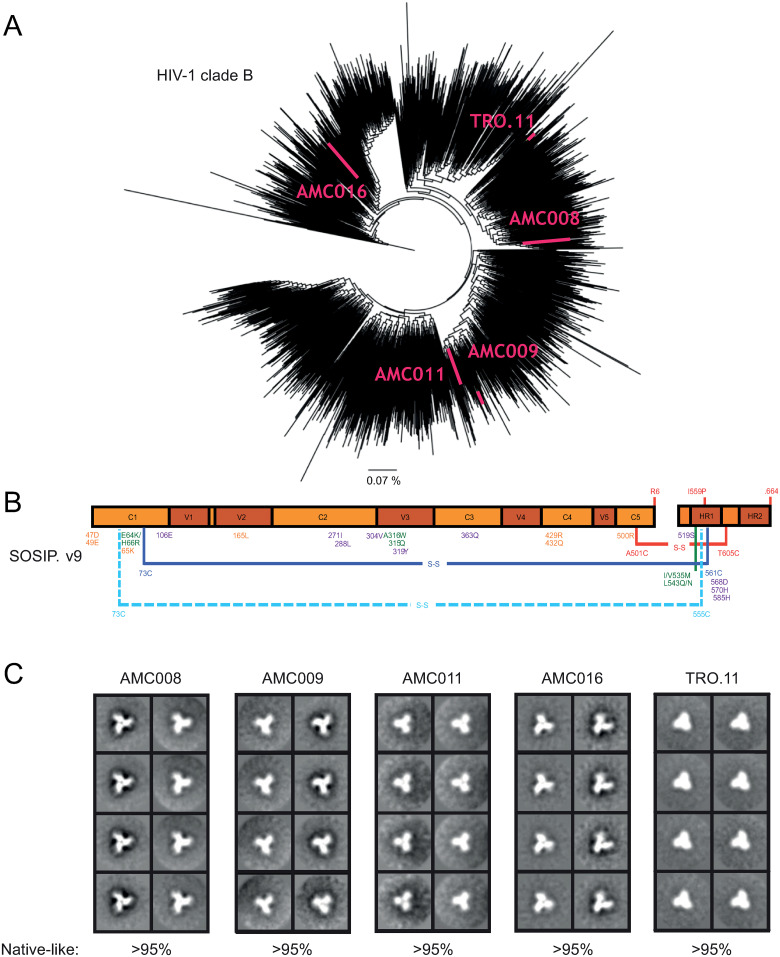
Fig 1. Clade B SOSIP.v9 proteins.
(A) Phylogenetic tree of HIV-1 clade B Env sequences. To make the tree, 2355 sequences were collected from the Los Alamos database. The sequences used in the study are indicated in pink. The line presents 0.07% difference. (B) Linear schematic of the SOSIP.v9 construct. Amino acid substitutions are indicated in different colors based on where they were first described. SOSIP.664 mutations are shown in red [40]. SOSIP.v4 mutations are indicated in green [15]. SOSIP.v5 mutations are indicated in dark blue [16]. SOSIP.v6 mutations are shown in light blue [16]. TD8 mutations are shown in yellow [38]. MD39 mutations are shown in purple [39]. The lines indicate intra-protomer disulfide bonds and the dashed lines indicate inter-protomer disulfide bonds. (C) 2D class-average negative-stain EM images of the five clade B SOSIP proteins. The percentage of native-like trimers found in each sample is indicated.