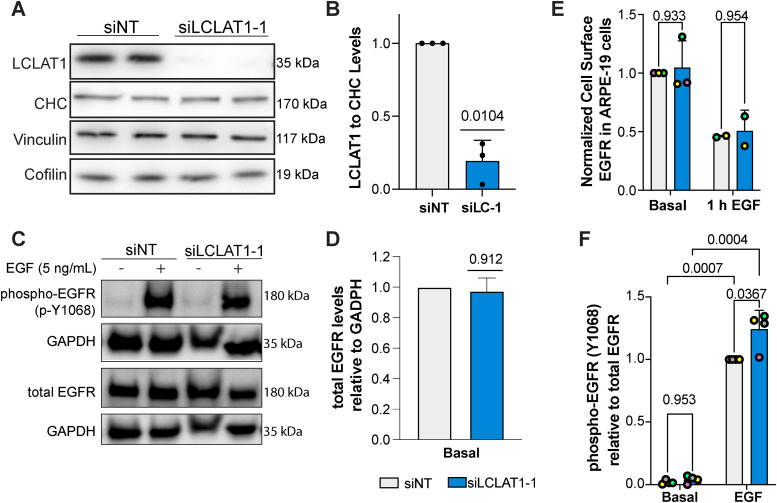
FIGURE 1:
LCLAT1 silencing has no negative impact on EGFR activation, EGFR total levels, and EGFR surface levels in ARPE-19 cells. (A) Western blots showing repressed LCLAT1 expression in ARPE-19 cells transfected with siLCLAT1-1 oligonucleotides relative to nontargeting control siRNA (NT siRNA). Two replicate lanes per condition are shown. Clathrin heavy chain (CHC), cofilin, and vinculin were used as loading controls. (B) Normalized ratio of LCLAT1 expression to CHC in ARPE-19 cells. (C) ARPE-19 cells silenced for LCLAT1 or treated with nontargeting oligonucleotide were serum-starved and then stimulated with 5 ng/ml EGF for 5 min. Lysates were then probed for total EGFR or phospho-EGFR. GAPDH was employed as the loading control. (D) Quantification of total EGFR relative to the respective GAPDH signal. (E) Normalized cell surface EGFR detected by immunofluorescence before and after 1 h stimulation with 100 ng/ml EGF in nontargeted and LCLAT1-silenced ARPE-19 cells. (F) Quantification of phospho-EGFR (p-Y1068) relative to the respective total EGFR signal. All experiments were repeated a minimum of three times except in E (EGF stimulation, n = 2). Data points from matching independent experiments are color coded. For B, D, and F shown is mean ± STD. Data in E are shown as mean ± SEM where at least 40–80 cells were scored per condition per experiment. Data in B and D were analyzed by a one-sample t test using hypothetical value of 1. For data in E and F, a repeated measures two-way ANOVA followed by Sidak’s (E) or Tukey’s (F) post-hoc test was used. p values are indicated.