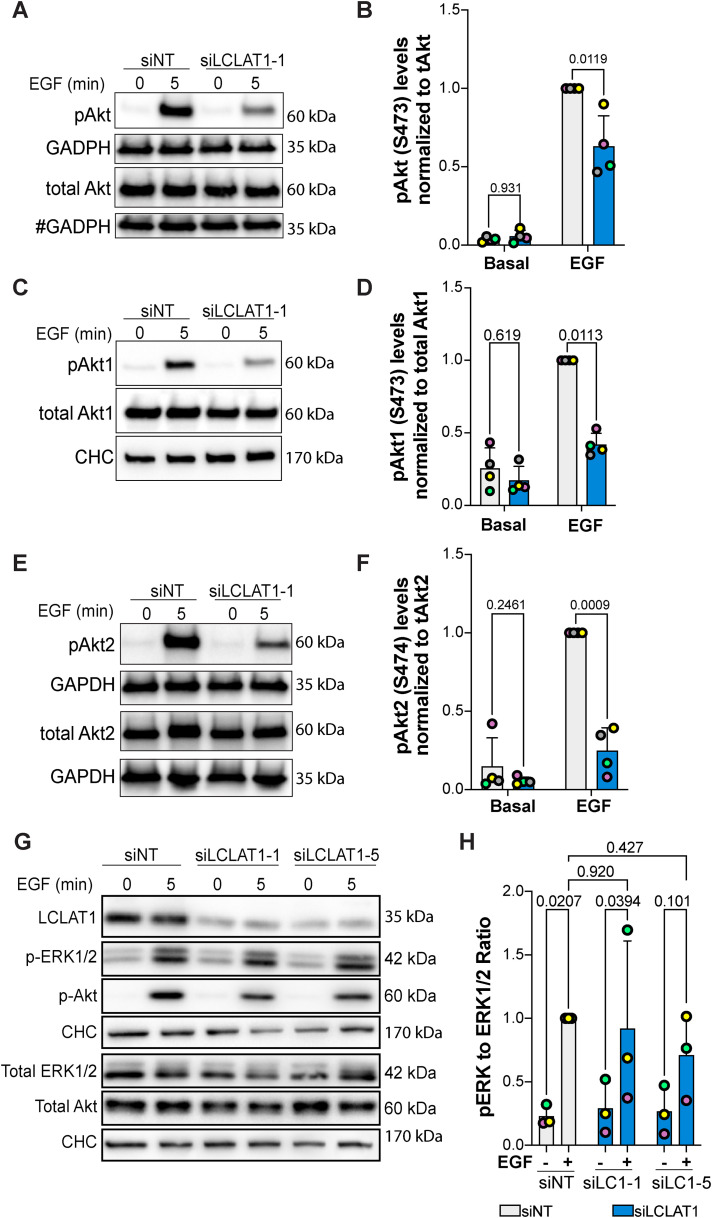
FIGURE 5:
LCLAT1 is required for EGF-stimulated Akt activation in ARPE-19 cells. (A, C, E) Mock-silenced (siNT) and LCLAT1-silenced ARPE-19 cells were serum-starved (0 min) or stimulated with 5 ng/ml EGF for 5 min. Lysates were then prepared, separated by SDS–PAGE and probed by Western blotting for pan-phospho-Akt and total pan-Akt (A), phospho-Akt1 and total Akt1 (C), and phospho-Akt2 and total Akt2 (E). Clathrin heavy chain (CHC) or GAPDH were used as loading controls. # indicates that the GAPDH blot was also used as loading control for p-TSC2 in Figure 7G since they originated from the same membrane cut across to probe for different sized proteins. (B, D, F) Quantification of pan-pAkt (B), pAkt1 (D), and pAkt2 (F) normalized to respective total pan-Akt, Akt1, and Akt2. (G) ARPE-19 cells transfected with nontargeting, LCLAT1-1, or LCLAT1-5 oligonucleotides and stimulated as above. Lysates were probed with LCLAT1, phospho-ERK1/2, ERK1/2, phospho-Akt, Akt, and CHC as loading control for each blot. (E) Quantification of phospho-ERK1/2 relative to total ERK1/2. Mean ± STD are shown from n = 4 (A, C, and E) and n = 3 (G) independent experiments are shown. Data points from matching independent experiments are color coded. Repeated measures two-way ANOVA and Sidak’s (B, D, F) or Tukey’s (H) post-hoc tests were used to statistically test the data. p values are indicated.