Abstract
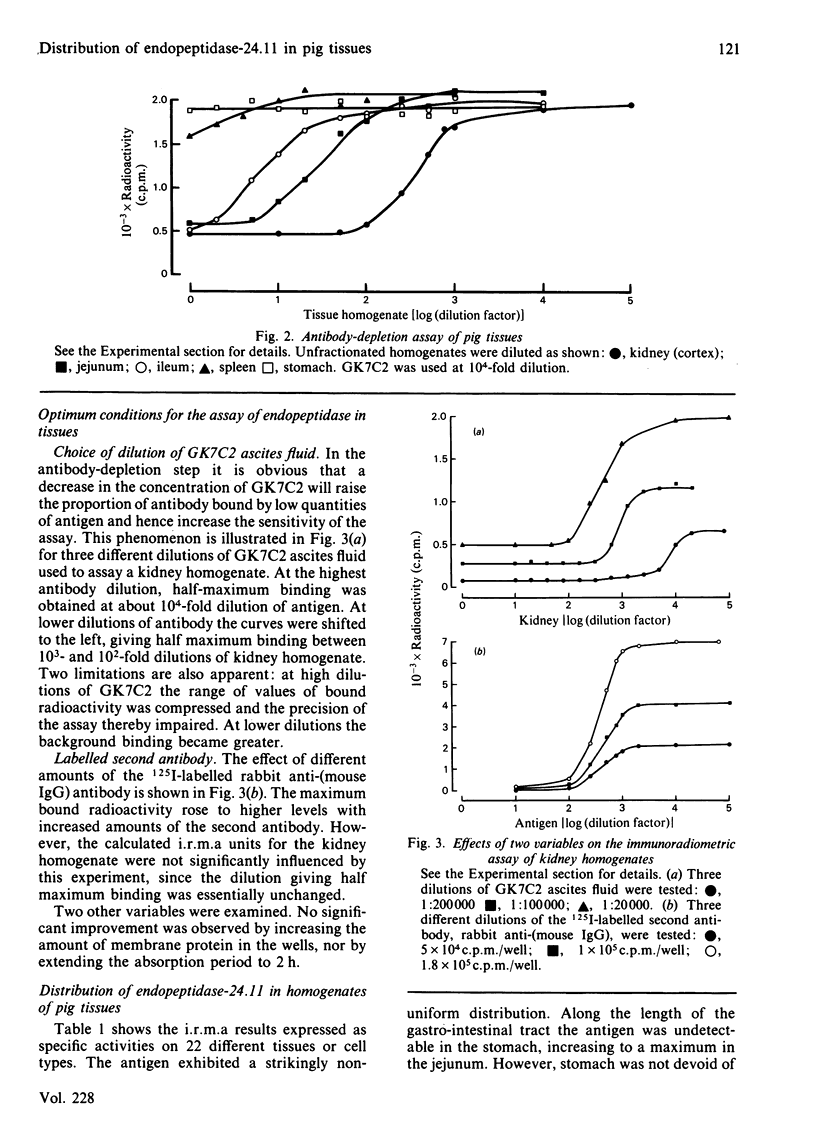
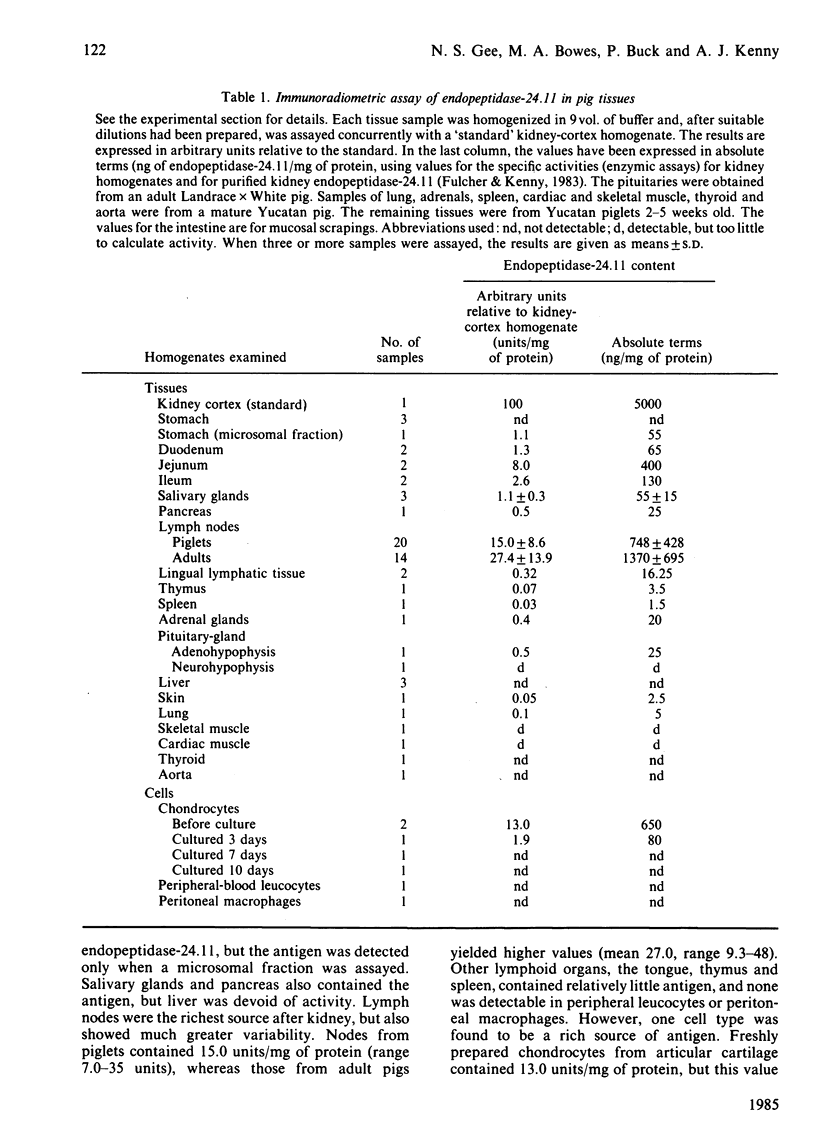
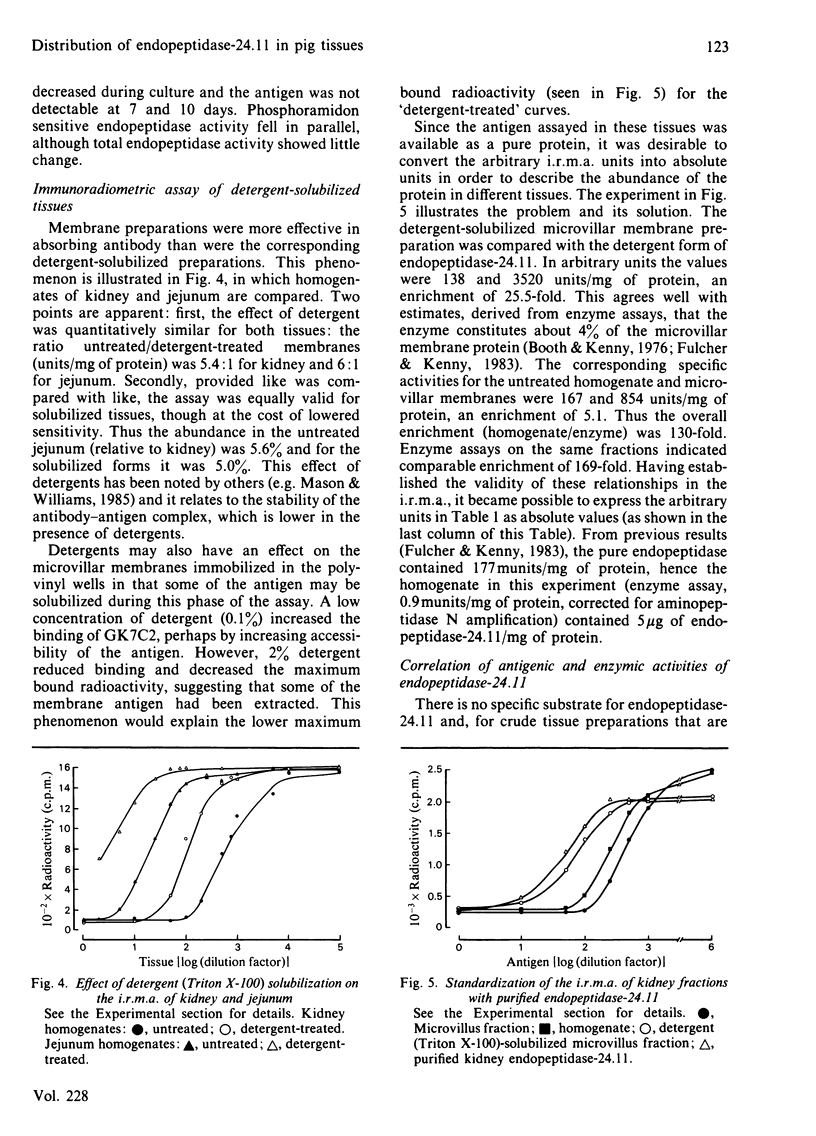
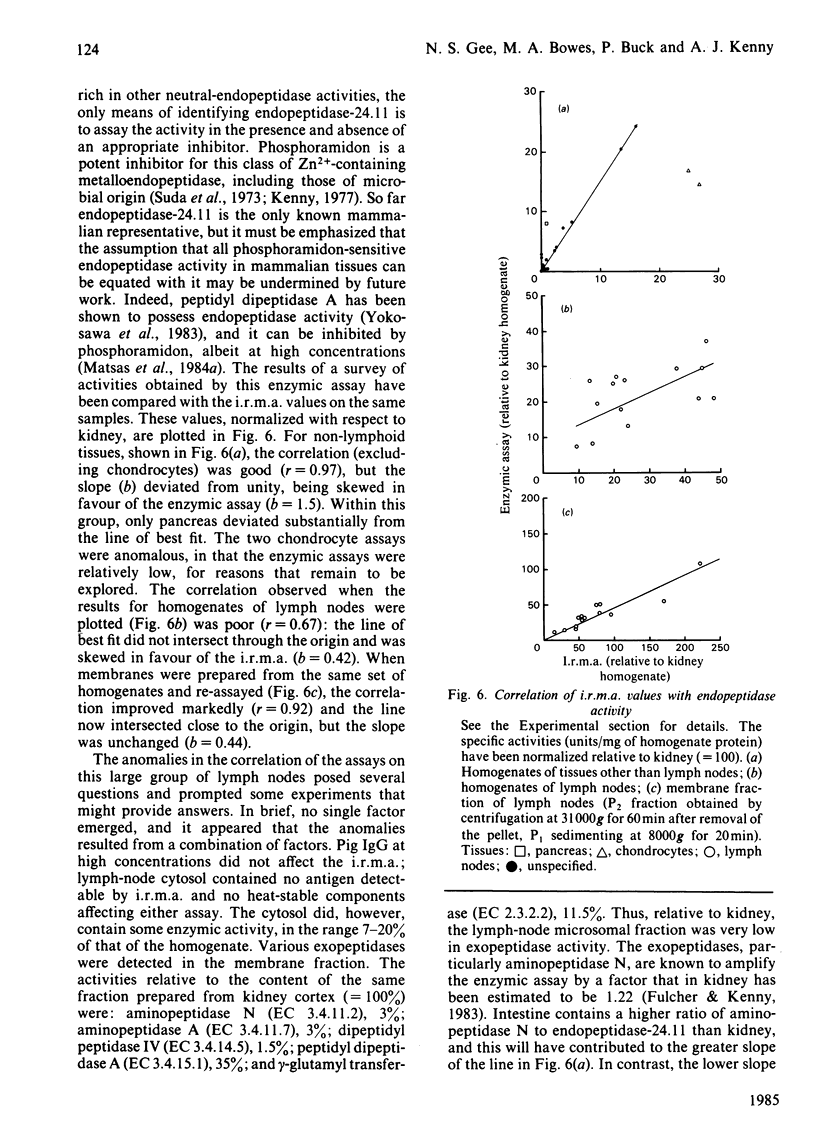
An immunoradiometric assay for endopeptidase-24.11, which depended on the absorption by tissues of a monoclonal antibody, GK7C2, was established. The optimum conditions for the assay were defined and its correlation with an enzymic assay determined. The immunoassay was used to survey the endopeptidase in crude homogenates of various tissues of the pig. Detergent treatment decreased the sensitivity of the assay but did not invalidate it. Although the endopeptidase was found in many tissues, it was neither uniformly nor ubiquitously distributed. Kidney cortex was confirmed as the major location of the endopeptidase, containing 5000 ng/mg of protein. Lymph nodes were also very active (1370 ng/mg), followed by chondrocytes from articular cartilage (650 ng/mg). In the gut, the endopeptidase was concentrated mainly in the jejunum (130 ng/mg). Various glands (salivary, adrenal, anterior pituitary and pancreas) also contained the antigen in the range 20-55 ng/mg of protein. Lung contained only 5 ng/mg of protein and, in other tissues examined, little or none was detectable. In particular, other lymphoid tissues (spleen, thymus, tonsillar tissues) were relatively poor sources, and none was detectable in peripheral-blood leucocytes or in peritoneal macrophages.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blalock J. E. The immune system as a sensory organ. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1067–1070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth A. G., Kenny A. J. A rapid method for the preparation of microvilli from rabbit kidney. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;142(3):575–581. doi: 10.1042/bj1420575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth A. G., Kenny A. J. Proteins of the kidney microvillus membrane. Identification of subunits after sodium dodecylsullphate/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. Biochem J. 1976 Nov;159(2):395–407. doi: 10.1042/bj1590395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsen E. M., Vyas J. P., Kenny A. J. A neutral endopeptidase in the microvillar membrane of pig intestine. Partial purification and properties. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 1;191(2):645–648. doi: 10.1042/bj1910645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher I. S., Chaplin M. F., Kenny A. J. Endopeptidase-24.11 purified from pig intestine is differently glycosylated from that in kidney. Biochem J. 1983 Nov 1;215(2):317–323. doi: 10.1042/bj2150317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher I. S., Kenny A. J. Proteins of the kidney microvillar membrane. The amphipathic forms of endopeptidase purified from pig kidneys. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 1;211(3):743–753. doi: 10.1042/bj2110743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gee N. S., Matsas R., Kenny A. J. A monoclonal antibody to kidney endopeptidase-24.11. Its application in immunoadsorbent purification of the enzyme and immunofluorescent microscopy of kidney and intestine. Biochem J. 1983 Aug 15;214(2):377–386. doi: 10.1042/bj2140377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George S. G., Kenny J. Studies on the enzymology of purified preparations of brush border from rabbit kidney. Biochem J. 1973 May;134(1):43–57. doi: 10.1042/bj1340043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny A. J., Fulcher I. S. Microvillar endopeptidase, an enzyme with special topological features and a wide distribution. Ciba Found Symp. 1983;95:12–33. doi: 10.1002/9780470720769.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr M. A., Kenny A. J. The purification and specificity of a neutral endopeptidase from rabbit kidney brush border. Biochem J. 1974 Mar;137(3):477–488. doi: 10.1042/bj1370477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsas R., Fulcher I. S., Kenny A. J., Turner A. J. Substance P and [Leu]enkephalin are hydrolyzed by an enzyme in pig caudate synaptic membranes that is identical with the endopeptidase of kidney microvilli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3111–3115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsas R., Kenny A. J., Turner A. J. The metabolism of neuropeptides. The hydrolysis of peptides, including enkephalins, tachykinins and their analogues, by endopeptidase-24.11. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 15;223(2):433–440. doi: 10.1042/bj2230433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsas R., Turner A. J., Kenny A. J. Endopeptidase-24.11 and aminopeptidase activity in brain synaptic membranes are jointly responsible for the hydrolysis of cholecystokinin octapeptide (CCK-8). FEBS Lett. 1984 Sep 17;175(1):124–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80583-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumford R. A., Pierzchala P. A., Strauss A. W., Zimmerman M. Purification of a membrane-bound metalloendopeptidase from porcine kidney that degrades peptide hormones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6623–6627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski M., Wilk S. Purification and specificity of a membrane-bound metalloendopeptidase from bovine pituitaries. Biochemistry. 1981 Aug 18;20(17):4942–4950. doi: 10.1021/bi00520a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Relton J. M., Gee N. S., Matsas R., Turner A. J., Kenny A. J. Purification of endopeptidase-24.11 ('enkephalinase') from pig brain by immunoadsorbent chromatography. Biochem J. 1983 Dec 1;215(3):519–523. doi: 10.1042/bj2150519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saklatvala J., Curry V. A., Sarsfield S. J. Purification to homogeneity of pig leucocyte catabolin, a protein that causes cartilage resorption in vitro. Biochem J. 1983 Nov 1;215(2):385–392. doi: 10.1042/bj2150385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suda H., Aoyagi T., Takeuchi T., Umezawa H. Letter: A thermolysin inhibitor produced by Actinomycetes: phospholamidon. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1973 Oct;26(10):621–623. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.26.621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trechsel U., Dew G., Murphy G., Reynolds J. J. Effects of products from macrophages, blood mononuclear cells and or retinol on collagenase secretion and collagen synthesis in chondrocyte culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jul 22;720(4):364–370. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(82)90113-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokosawa H., Endo S., Ogura Y., Ishii S. A new feature of angiotensin-converting enzyme in the brain: hydrolysis of substance P. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Oct 31;116(2):735–742. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90586-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


