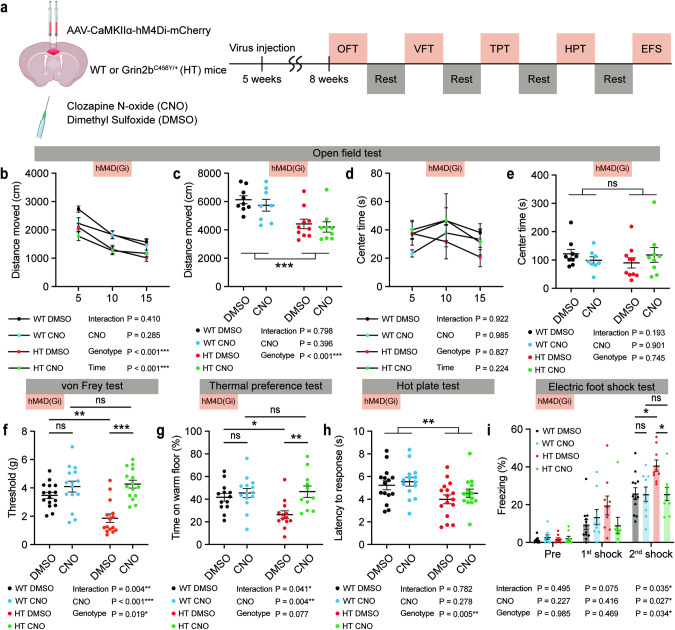
Fig. 4. Chemogenetic ACC inhibition normalizes sensory hypersensitivity in Grin2bC456Y/+ mice.
a Schema of chemogenetic modulation using DREADD. Injection of AAV-CaMKIIα-hM4Di-mCherry into the WT and Grin2bC456Y/+ ACC was followed by locomotor and sensory tests with CNO/DMSO treatment. b–e Chemogenetic inhibition of ACC neurons does not alter the open-field locomotion and anxiety-like behavior (center time) of Grin2bC456Y/+ mice (2–3 months) (n = 9 mice [WT-DMSO], 8 [WT-CNO], 10 [HT-DMSO], 9 [HT-CNO], three-way ANOVA [distance moved/center time], two-way ANOVA [total distance moved/center time]). f–i Chemogenetic inhibition of ACC neurons normalizes the sensory hypersensitivity of Grin2bC456Y/+ mice (2–3 months) in the electronic von Frey, thermal place-preference, and electric foot-shock tests but not in the hot-plate test (n = 16 mice [WT-DMSO], 15 [WT-CNO], 15 [HT-DMSO], 15 [HT-CNO] for von Frey, 13, 13, 15, and 12 [thermal place preference], 15, 14, 16, and 14 [hot-plate], 12, 9, 9, and 9 [electric foot-shock], two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test [von Frey, thermal place-preference], two-way ANOVA [hot-plate], two-way ANOVA with/without Tukey’s test [electric foot-shock; significant genotype x drug interaction for the 2nd but not 1st shock]). Significance is indicated as * (<0.05), ** (<0.01), *** (<0.001), or ns (not significant).