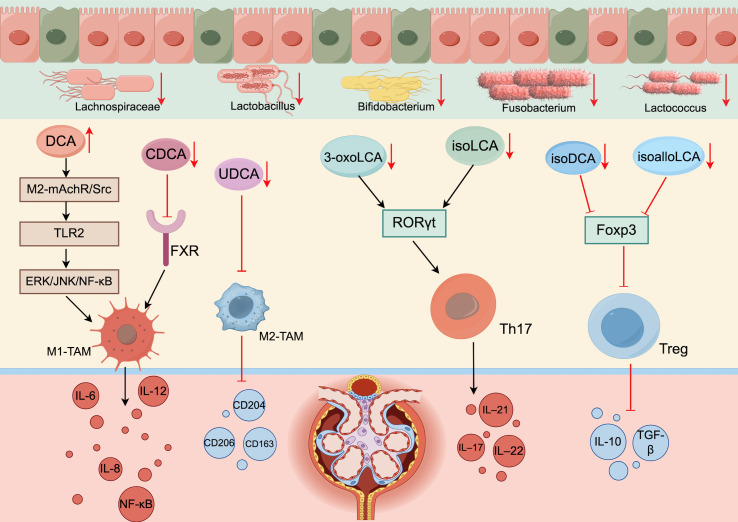
Figure 2.
Disturbances in bile acid metabolism disrupt immune cell homeostasis (generated by Figdraw 2.0). When the intestinal flora of DKD patients is disrupted, the number of bacteria involved in bile acid synthesis and enterohepatic circulation is reduced, which affects the activity of various enzymes and reduces secondary bile acid synthesis. Bile acid acts as the endogenous ligand of FXR/TGR5; thus, reduced bile acid synthesis inhibits the activation of FXR/TGR5. In addition, an imbalance in the intestinal flora disrupts bile acid metabolism by inhibiting ABST expression.