Figure 6. Case examples for Class Distribution.
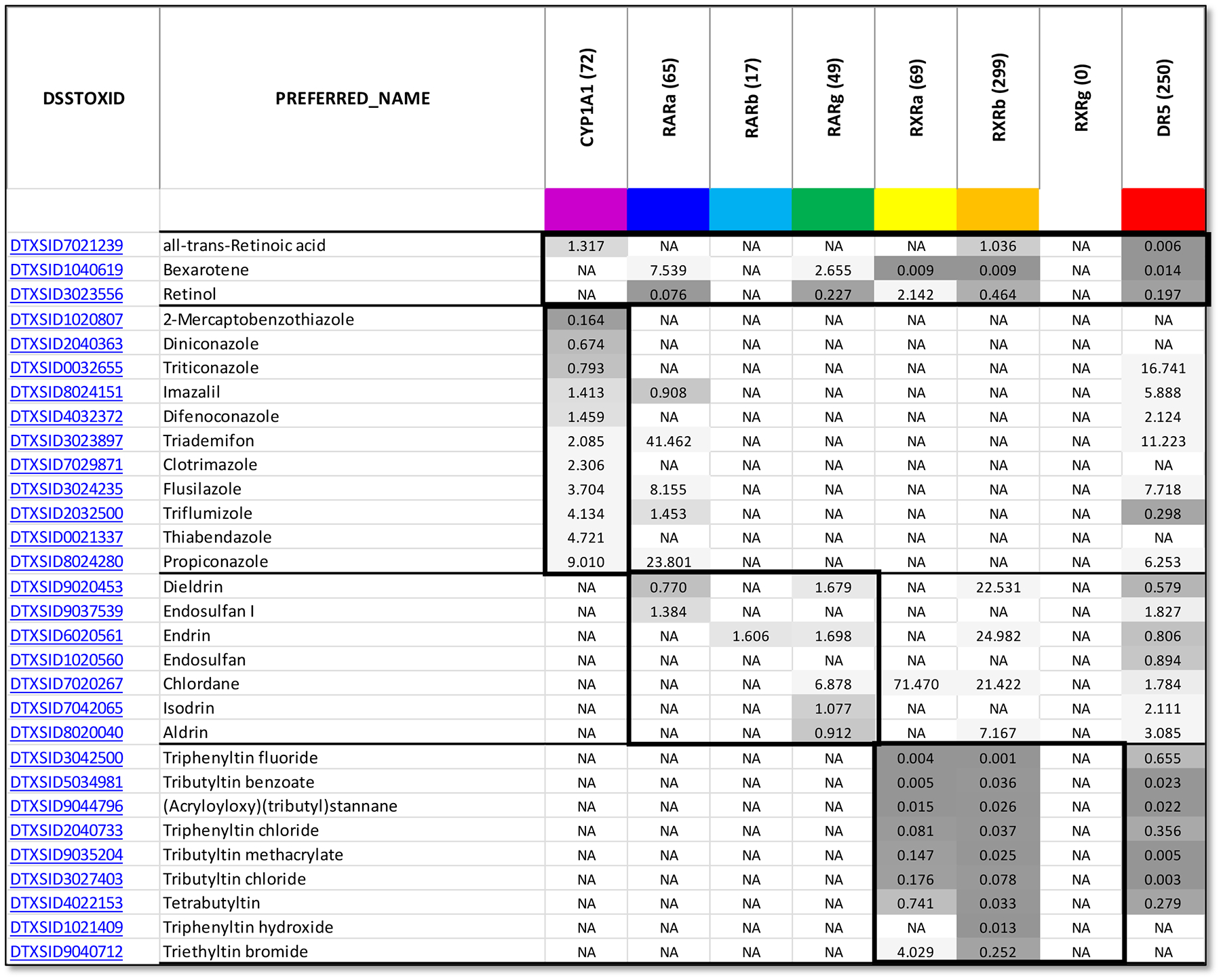
Distribution from chemical hits (n=261) having AC50 < 2 μM in one or more of the 8 ToxCast assays (Baker, Boobis et al. 2018). Each assay target is indicated with the number of chemical his registered in the EPA CompTox Chemicals Dashboard (https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard, last accessed October, 2020). CYP1A1: NVS_ADME_hCYP1A1. RARs: ATG_RARa_TRANS_up, ATG_RARb_TRANS_up, ATG_RARg_TRANS_up. RXRs: ATG_RXRa_TRANS_up, ATG_RXRb_TRANS_up, ATG_RXRg_TRANS_up. DR5: ATG_DR5_CIS_up. As might be expected the DR5 lights up several potential RAR/RXR combinations. First group: vitamin A (retinol) and retinoid ligands (ATRA/RAR, Bexarotene/RXR) references. Second group: Triazole effects on biochemical activity of CYP1A1 as a surrogate for CYP26 isoforms; malformations, vertebral transformations, and caudal regression are linked to CYP26 inhibition (Menegola, Broccia et al. 2001, Kamata, Shiraishi et al. 2008, Tonk, Pennings et al. 2015). Third group: several organochlorine pesticides of a persistent nature have weak RARg-agonist activity and can transactivate retinoid-responsive genes (e.g., CYP26A1) via RARE (Lemaire, Balaguer et al. 2005, Kamata, Shiraishi et al. 2008). Fourth group: several organotin biocides are known to preferentially bind RXRs with nM affinity, but forms a non-permissive RAR/RXR heterodimer (Grun, Watanabe et al. 2006, Brtko and Dvorak 2015).
