FIG. 4.
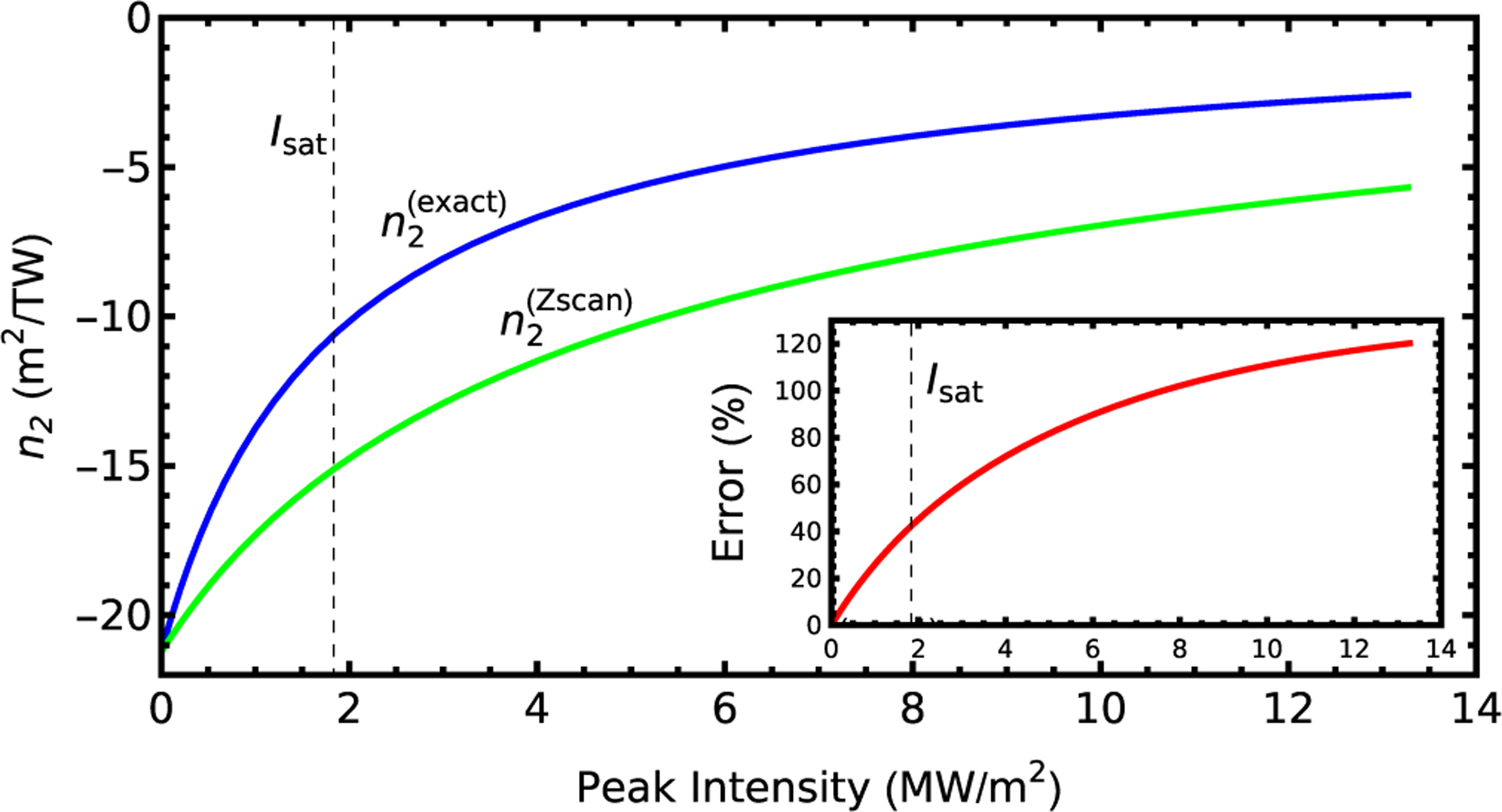
The Kerr coefficient is calculated (, blue) as a function of the peak intensity for a two-level system for the conditions given in the text; (, green) is determined by finding the -scan curve given the intensity-dependent Kerr coefficient presented here, finding the peak-valley difference on this curve, interpreting this peak-valley distance using low-intensity -scan theory, multiplying by constant factors following the procedure of McCormick et al. [8] for determining . The inset shows the systematic error of this procedure using . The saturation intensity is marked at which corresponds to .
