FIG. 9.
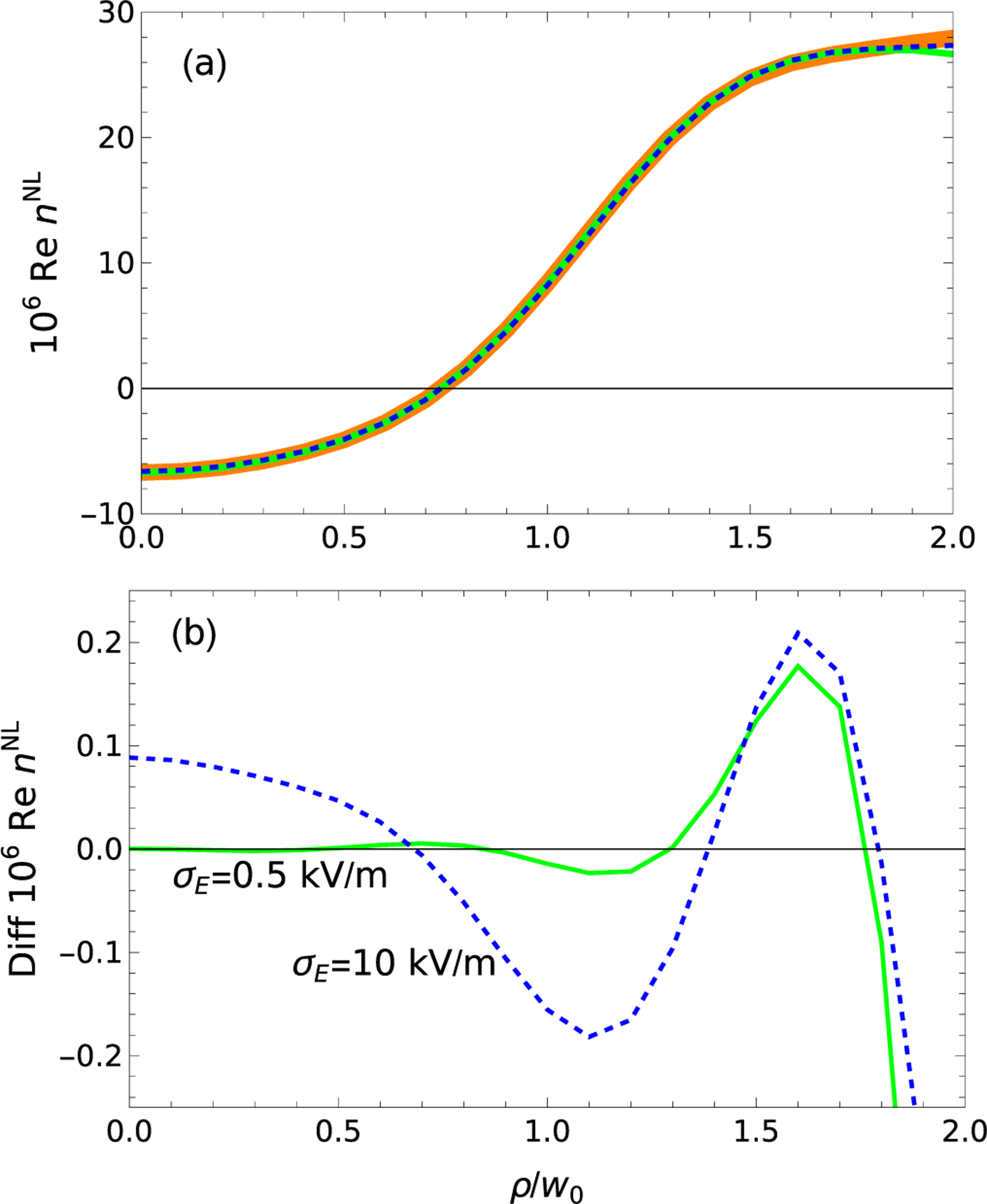
(a) The saturated Kerr coefficient as a function of the electric field, including (black) the exact expression for the two-level system as in Fig. 7, and values found with PROM using 12 basis assuming the incident electric field varies by (thick orange) 0, (green) 0.5%, and (dashed blue) 10%. There is no detector noise. The calculation uses 21 point Gaussian integration. In panel (b), the differences of the curves with 0.5 and 10% electric-field fluctuations from the noise-free answer are shown. The calculation was done with the computational convention, so differences in Re are meaningful, but not the value itself. Since all calculations use the same convention, intercomparisons are meaningful.
