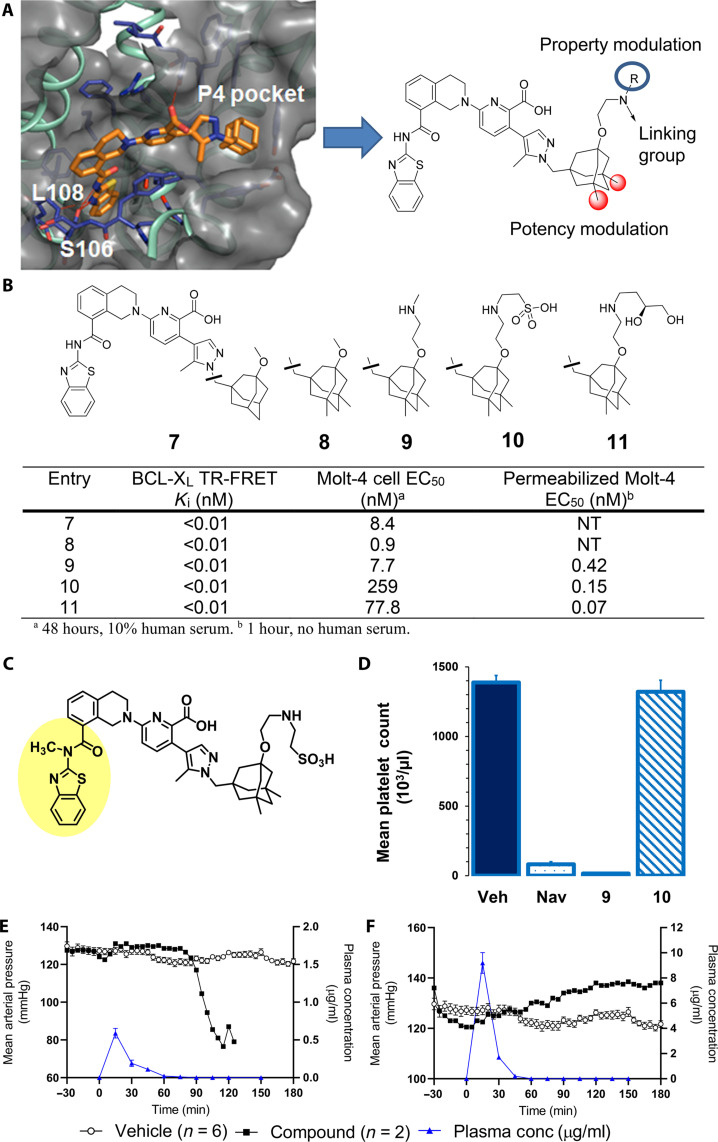
Fig. 2. Discovery of linkable BCL-XL inhibitors with different solubility and permeability properties affords putative ADC payload component with high target affinity yet minimal systemic toxicity in mice and dogs.
(A) X-ray cocrystal structure of BCL-XL bound to A-1331852 (1.93 Å; Protein Data Bank code 9AQZ; see the Supplementary Materials) and key regions of the BCL-XL inhibitor pharmacophore for modification as derived from the x-ray structure. (B) Binding, cellular potency in Molt-4 cells, and functional potency in digitonin-permeabilized Molt-4 cells of BCL-XL inhibitors. (C) Structurally related inactive inhibitor 11; methylation of P2-binding amide bond nitrogen disrupts key hydrogen binding network and leads to full ablation of cellular activity. (D) Platelet count 6 hours after treatment with BCL-XL inhibitors in heparinized whole mouse blood. Navitoclax (50 mg/kg) was given orally, and 9 (0.2 mg/kg) and 10 (0.6 mg/kg) were intravenously administered. Each bar represents the average platelet count in five SCID/bg mice. Error bars depict the SEM. (E and F) MAP of dogs administered vehicle (black filled circles) or BCL-XL inhibitor (open circles) and plasma concentration of BCL-XL inhibitors (blue triangles) following an intravenous bolus dose of either 9 or 10.