Fig. 5 |. An emVar at the HLA locus shows cell type-specific and allele-specific protein binding.
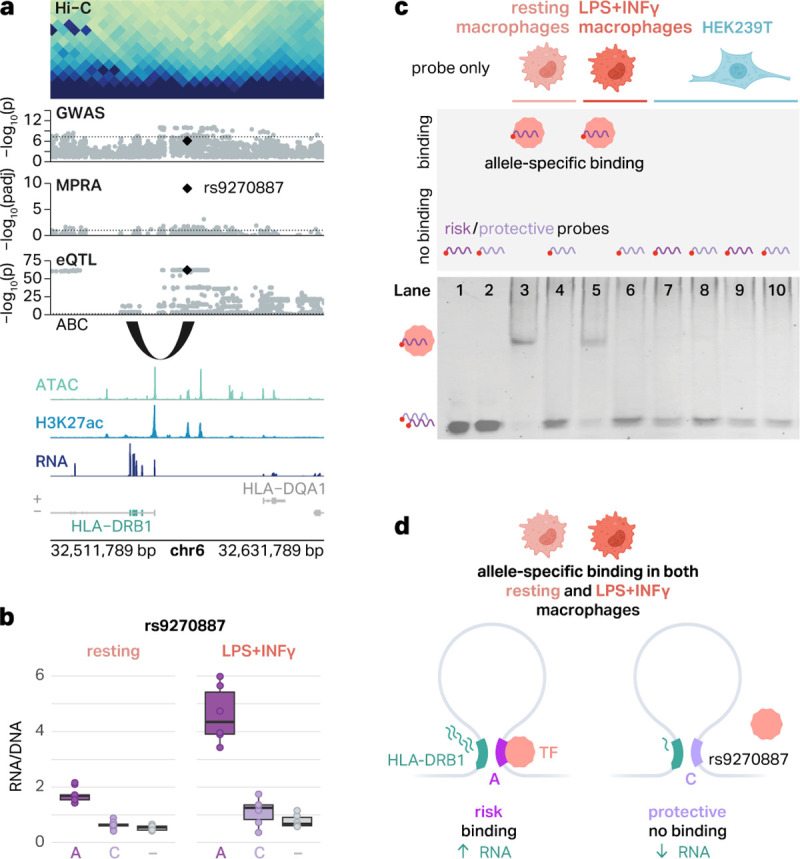
a, The emVar rs9270887 in the HLA gene cluster is connected to HLA-DRB1 via the ABC model and eQTLs. ATAC, H3K27ac, and RNA signal tracks have been merged across both conditions. b, Box plots show the transcriptional activity of risk and protective alleles of rs9270887 in resting and LPS+INFγ-treated macrophages compared to negative controls (−). The boxplots show the median and IQR with whiskers extending to the most extreme non-outliers. c, Graphical representation of experimental conditions and bands detected in EMSAs (top) and EMSA results for the emVar rs9270887 (bottom). Lanes 1–2, risk (1) and protective (2) probes without lysates. Lanes 3–4, risk (3) and protective (4) probes with lysates from resting macrophages. Lanes 5–6, risk (5) and protective (6) probes with lysates from LPS+INFγ-treated macrophages. Lanes 7–8, risk (7) and protective (8) probes with HEK293T lysates. d, Schematic of our suggested mechanism of regulation of HLA-DRB1. In THP-1 macrophages, there is a chromatin loop connecting rs9270887 to the promoter of HLA-DRB1. The risk A allele leads to increased transcription of GFP, likely due to TF binding. The protective C allele breaks this TF binding site, which is associated with decreased transcription of GFP.
