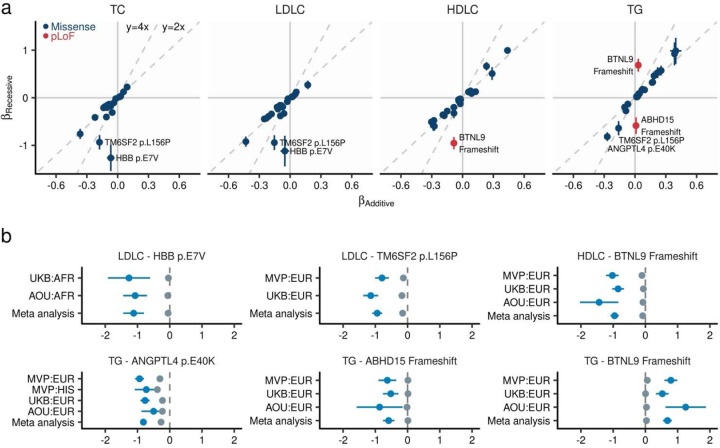
Fig. 4 |. Recessive alleles associated with blood lipids.
a. Comparison of effect sizes between additive and recessive models. The horizontal axis displays the effect size as estimated by linear mixed model under additive assumption, while the vertical axis shows the effect size estimated under recessive assumption (Methods). Each dot indicates a genetic variant, with the error bar representing the 95% confidence interval. Dashed lines represent the predictions of recessive effect sizes based on the additive model estimates (y = 2x) and estimates that are twice as large (y = 4x) as those from the additive model. b. Effect size from population-wise or meta-analysis estimates for variants with the largest deviations in recessive estimates from the predicted effect sizes based on additive model estimates. Gray dots represent additive effect sizes, while dark blue dots correspond to recessive effect sizes calculated by linear mixed model. Error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals. TC, Total Cholesterol; LDLC, Low Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol; HDLC, High Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol; TG, Triglycerides; MVP, Million Veteran Program; UKB, UK Biobank; AFR, African-like population; AMR, Admixed-American-like population; ASN, Asian-like population; EAS, East-Asian-like population; EUR, European-like population; HIS, Hispanic-like population; SAS, South-Asian-like population.