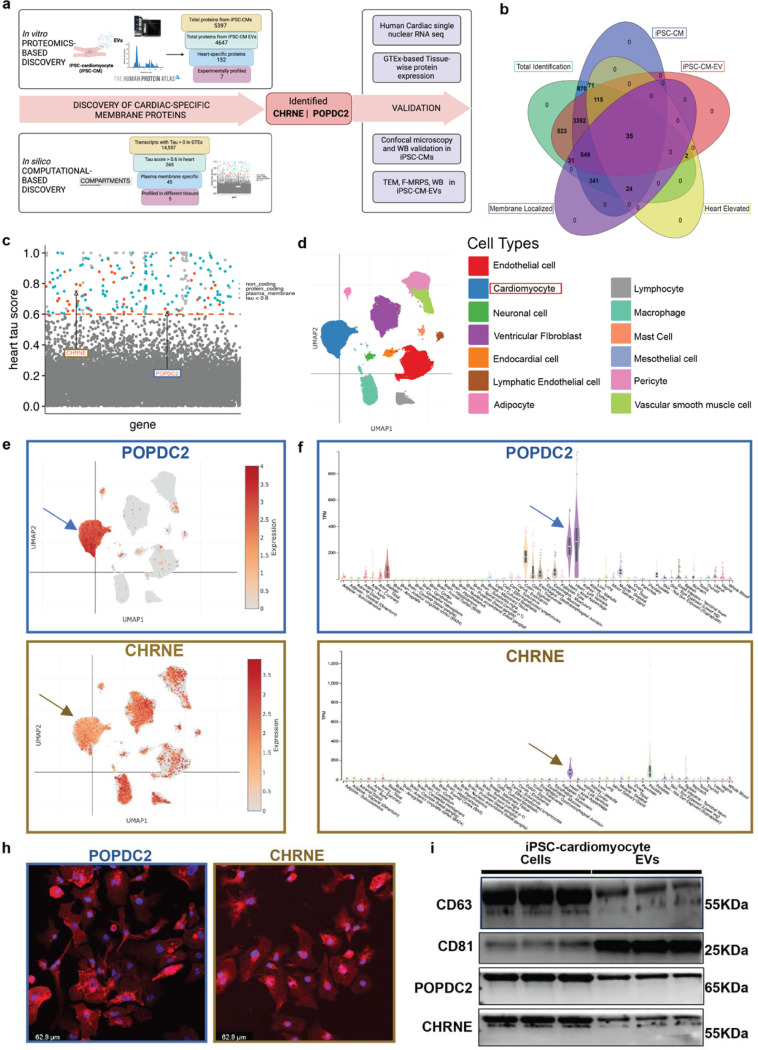
Figure 2. Discovery and experimental validation of POPDC2 and CHRNE as cardiomyocyte- EV (Extracellular Vesicle) membrane protein candidates.
a. Analytic scheme for identification and validation of cardiomyocyte EV membrane markers POPDC2 and CHRNE using step-wise proteomic-based and bioinformatic-based discovery followed by experimental validation in iPSC-CM cells and EVs. b. Venn diagram showing 35 targets that were identified using LC-MS/MS (Liquid Chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry) present in iPSC-CM (induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-derived Cardiomyocytes), iPSC-CM-EVs and prioritized by heart enrichment (from Human Protein Atlas data) and membrane-localization (Deep Transmembrane Helix Prediction). c. Scatter plot showing candidates from computational analysis obtained by mining GTEx for proteins with cardiac-specificity (tau) ≥ 0.6 (dots above the red dashed line) with red indicating protein-coding candidates present in the plasma membrane (predicted using Compartments). POPDC2 and CHRNE are indicated on the plot. d. UMAP (Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection) legend of cardiac single nuclear RNA-seq dataset from Broad single cell Portal. e. POPDC2 and CHRNE UMAPs demonstrating their expression in cardiomyocytes. f. Tissue-wise transcriptomic expression of POPDC2 and CHRNE using GTEx showing elevated expression in heart tissue. h. Representative confocal images showing the expression of POPDC2 and CHRNE proteins in iPSC-CMs. i. POPDC2 and CHRNE protein expression shown in iPSC-CMs and iPSC-CM-EVs by western blotting (n=3 independent experiments).