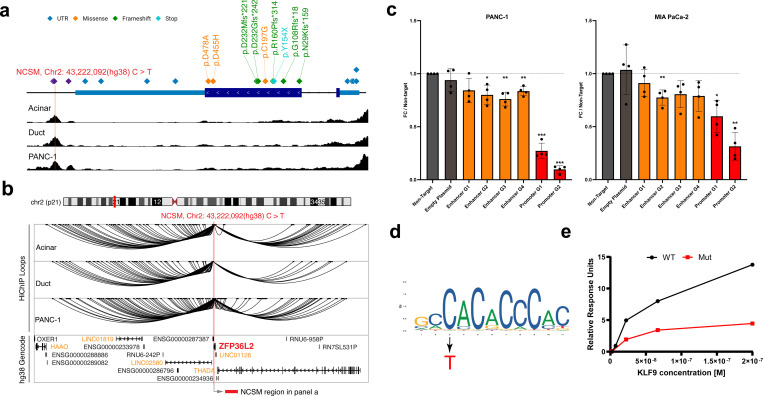
Fig. 6. Potential noncoding driver mutations at chr2p21.
a, A schematic illustration showing a NCSM (Hg38 chr2:43,222,092 C>T; Hg19 chr2:43,449,231) in an enhancer downstream of ZFP36L2. Additional mutations were located within the genes’ promoter, 5’UTR, exons, 3’UTR and the same downstream enhancer. The lower panel shows peaks of accessible chromatin (from ATAC-seq) in pancreatic acinar cells, pancreatic duct cells and PANC-1 cells (ATAC-seq results were similar in all other cell lines included in the study). b, Potential targets genes for the NCSM (chr2:43,222,092 C>T) assessed by H3K27ac HiChIP-seq in pancreatic acinar, ductal and PANC-1 cell lines. Interacting genes are listed in light orange text. C, CRISPRi targeting the mutated enhancer (dark orange) with four RNA guides as well as the promoter (red) of the gene with two guides in PANC-1 and MIA PaCa-2 cells. d, JASPAR DNA binding motif for KLF9 (MA1107.3) with the C>T mutation indicated (red). e, Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) results showing ~3-fold lower binding of recombinant KLF9 protein to a oligo representing the mutation at chr2:43,449,231 (Hg19) and surrounding DNA sequence. Coordinates are based on human reference build hg19 except in panels a and b.