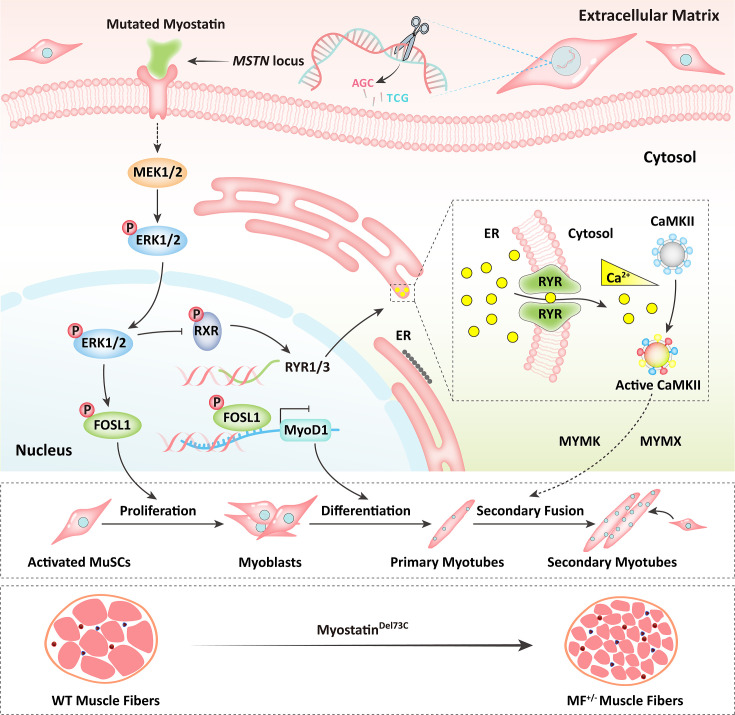
Figure 9. Schematic illustration of the regulation of muscle phenotypes by MSTNDel73C mutation with FGF5 knockout.
The MSTNDel73C mutation with FGF5 knockout mediated the activation of FOSL1 via MEK-ERK-FOSL1 axis. The activated FOSL1 promotes skeletal muscle satellite cell proliferation and inhibits myogenic differentiation by inhibiting the expression of MyoD1, and resulting in fusion to form smaller myotubes. In addition, activated ERK1/2 may inhibit the secondary fusion of myotubes by Ca2+-dependent CaMKII activation pathway, leading to myoblasts fusion to form smaller myotubes.