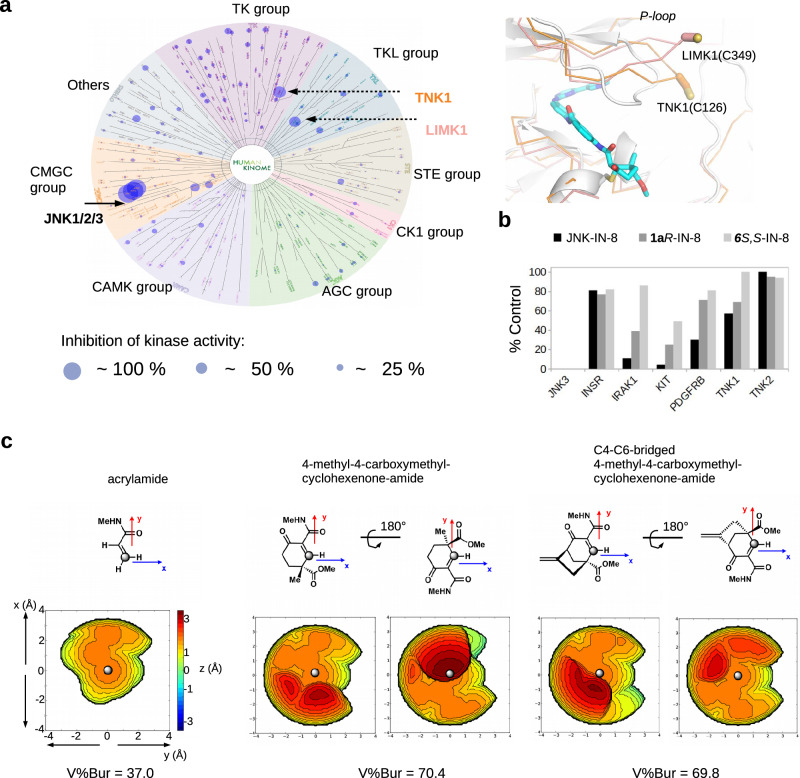
Fig. 5. Specificity of 1aR-IN-8 in the human kinome panel and analysis of steric congestion near the reactive center of open-chain versus cyclic warheads.
a Results of the Wild Type Kinase Panel (Reaction Biology Corp, USA; 340 human kinases) with 1aR-IN-8 used at 1 μM concentration. Inhibition of a specific kinase is depicted with a circle on the human kinome tree, where circle size correlates with the amount of inhibition. The panel on the right shows the structural models of LIMK1 (PDB ID: 3S95) and TNK1 (homology model created by AlphaFold 2) superimposed with the JNK1–1aR-IN-8 crystallographic model. LIMK1 and TNK1 are the only two human off-target kinases whose activity were inhibited more than 50% (see Supplementary Table 2). b Off-target kinase panel (1 target + 6 off-target kinases) and compound binding tested by the DiscoverX platform. Compounds were used in 1 μM concentration. Note that JNK3 is the target kinase and interacted strongly with all three inhibitors (its %Control value is 0 for all three compounds which is invisible in the bar graph). For %Control lower numbers indicate stronger binding of the compound to the tested kinase (where 0 means complete binding and 100 means no binding of the test compound to the kinase; the value shows the mean of duplicate measurements). (INSR: insulin receptor, IRAK1: interleukin 1 receptor associated kinase 1, KIT: c-KIT receptor tyrosine kinase, PDGFRB: platelet derived growth factor receptor beta, TNK1: tyrosine kinase non-receptor 1, TNK2: tyrosine kinase non-receptor 2, also known as ACK1). c Topographic steric maps of selected simplified warheads and buried volume calculation (V%Bur). Steric maps are derived from the DFT-optimized structures (see Supplementary Note 1). The isocontour scheme is in Å and a coloring scheme from dark red to deep blue is used to display sterically encumbered regions around the reactive center. The gray dot shown at the center of the xy plane represents the reactive carbon atom in the Michael acceptor and the steric map is viewed down the z-axis. Comparison of the steric maps of the simplified warheads indicates that the establishment of the cyclic form notably increases steric congestion and/or reshapes the encumbered region near the reactive center. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.