Fig. 6. JNK isoform specificity of cyclohexenone warhead containing inhibitors.
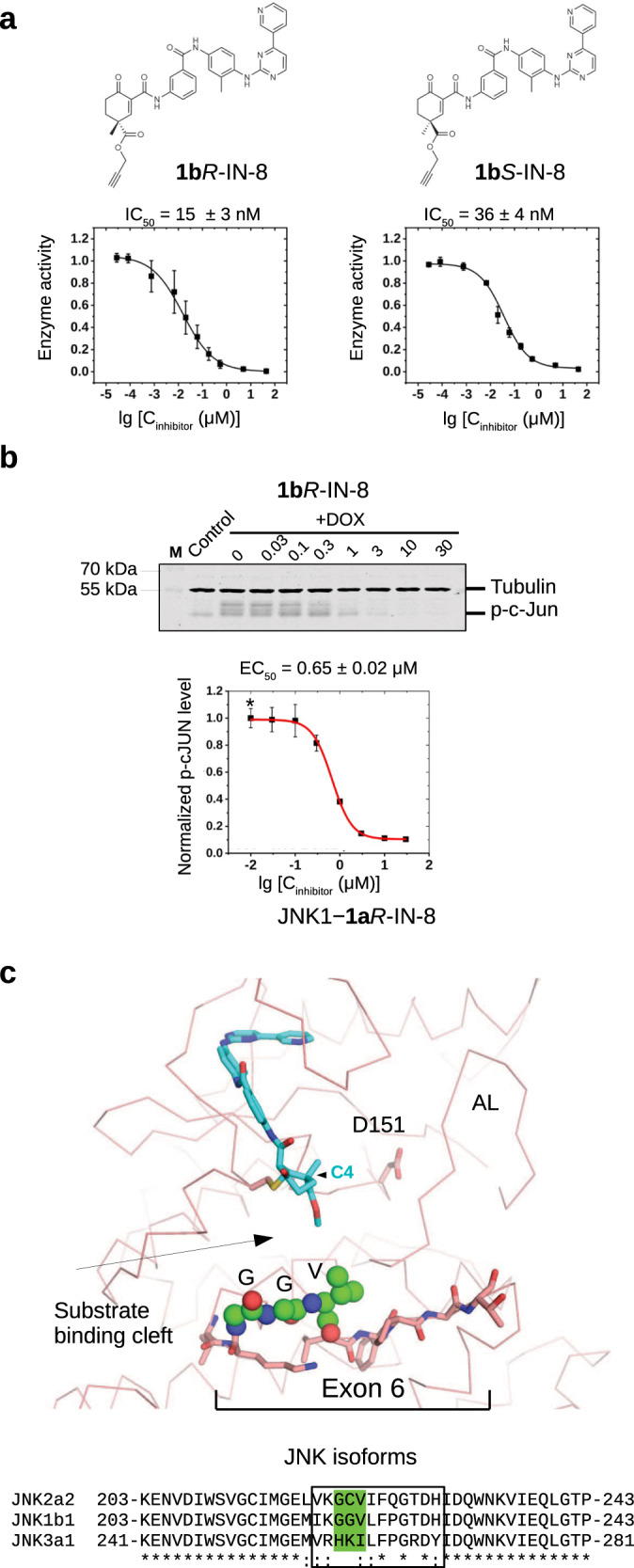
a PhALC assay results with 1bR-IN-8 and 1bS-IN-8. These compounds contain a propargyl ester moiety allowing further C4 extensions by either CuAAc click chemistry or by Sonogashira coupling (see Supplementary Fig. 14). Error bars show SD (n = 3, independent experiments). b Results of the in-cell c-Jun phosphorylation assay with 1bR-IN-8. The Western-blot panel shows the results of one experiment. Data show the mean value and error bars show SD on the graph (n = 3, three independent experiments). Note that the EC50 of this modestly C4-extended compound displays similar inhibitory capacity compared to 1aR-IN-8 (see Table 1). c The structural panel shows the crystal structure of the JNK1–1aR-IN-8 complex highlighting residues corresponding to exon 6 (shown with stick representation). This short region varies among JNK isoforms, and it forms the base of the substrate binding cleft next to the active site (D151). The three residues (GGV) displaying the greatest variation among the examined JNK isoforms are shown with spheres on the structural panel. Note that the substrate binding cleft is remodeled upon JNK activation loop (AL) phosphorylation, but the region corresponding to exon 6, especially the residues shown with spheres, will stay in the proximity of the cyclohexenone warhead. Inhibitor contacts will likely be affected by the stereochemistry of the warhead and/or the length of the substituent groups at C4. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.
