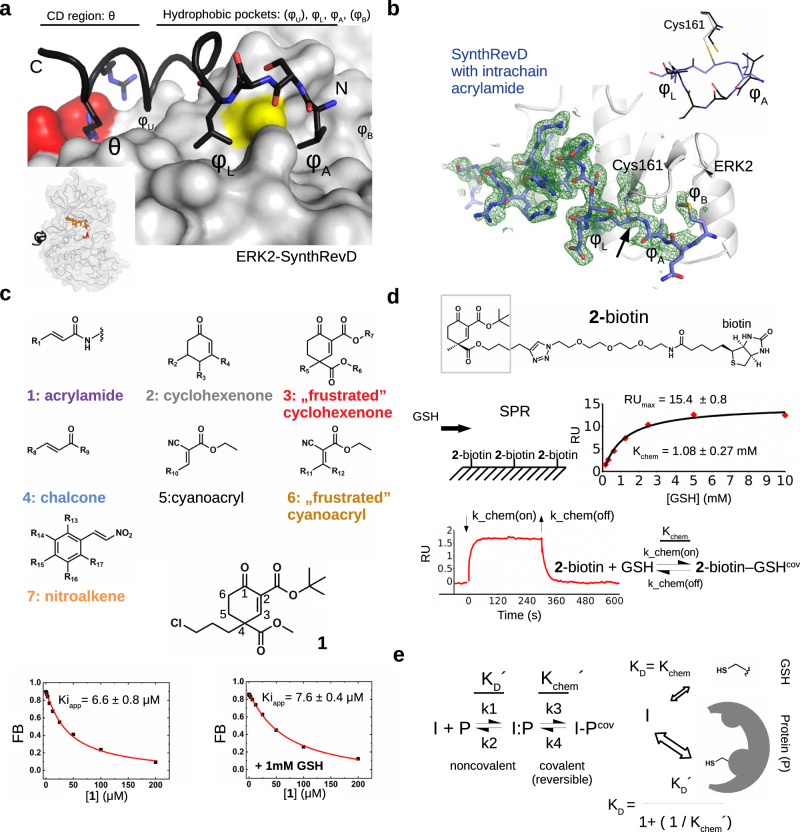
Fig. 1. Covalent binding of sterically crowded cyclohexenon compounds in the MAPK D-groove is resilient to GSH.
a Topography of the MAPK D-groove. The negatively charged aspartate residues (D318 and D321) are colored red, Cys161 is colored yellow. The panel on the left shows the crystal structure of the ERK2-SynthRevD protein-peptide complex (PDB ID: 4FMQ)20. The inset shows the position of the D-peptide (in black), the nucleotide (in orange) and the catalytic region (D149; in red). b Crystal structure of ERK2 with an acrylamide containing artificial peptide (SynthRevDCOV; PDB ID: (8PSR). The panel shows the Fo-Fc omit map (2ϭ) calculated with the final model but without the peptide-cysteine adduct. The inset shows the region between φL and φA for the free (SynthRevD, black) or the Michael acceptor (intrachain acrylamide) containing covalently bound peptide (SynthRevDCOV, blue). c Gallery of the Michael acceptor warheads represented in the compound collection (Group 1-7) with the structure of one of the hit compounds from Group 3 (1). Capacity of the small molecule to block ERK2 binding to a fluorescently labeled D-peptide probe was monitored in a quantitative binding assay. Panels below show competitive binding curves with 1 in the absence or presence of 1 mM GSH. Kiapp is a proxy for the MAPK binding affinity of unlabeled compounds. (FB: Fraction Bound; error indicates the parameter estimation error based on the least square method, n = 3). d Binding of GSH to a cyclohexenone-based warhead. 2-biotin was immobilized on the SPR streptavidin chip by biotin capture and GSH was injected over the chip surface at different concentrations. The panel shows the equilibrium binding data (with red diamonds) fitted to a 1:1 stoichiometric binding model (in black line). The expected RUmax at the applied capture level is ~15, the error of the determined KD and the RUmax shows the parameter estimation error based on the least square method. The panel below shows the results of a kinetic binding experiment with 1 mM GSH injected over the chip with lower 2-biotin capture level (RUmax is ~3.5; result of one representative experiment). Based on this measurement k_chem(off) is 0.07 s−1 using the 1:1 reversible binding model. The association rate falls outside the reliable measurement range of the instrument (>1000 M−1s−1), but if Kchem is 1 mM, based on the equilibrium measurement, then k_chem(on) is ~70 M−1s−1. e The scheme of reversible inhibitor (I) binding to a cysteine thiol on the surface of a protein (P). The equilibrium constants based on this 2-step scheme for the formation of I-Pcov complex as well as the corresponding kinetic rates are shown on the left. The two formulas below represent the overall KD expressed in different forms for the I (inhibitor) + P (protein) reaction where I is a reversible covalent inhibitor. The formula on the right can be obtained from the classical definition of KD shown on the left with the equilibrium concentrations of the different species in steady-state. A division of the latter by [I:P] leads to the following formula: ([P] * [I] / [I:P]) / (1 + ([I-Pcov] / [I:P])), where ([P] * [I]) / [I:P] equals to KD´ and [I-Pcov] / [I:P] is equal to Kchem´ by definition, giving the final equation KD = KD´ / (1 + (1/Kchem´)) that can be used to describe the binding of a reversible covalent inhibitor to a protein surface thiol. Kchem´ is characteristic for the activity of the inhibitor to form the reversible covalent bond with the target thiol, while KD´ is characteristic for noncovalent contact formation of the inhibitor on a protein surface surrounding the thiol of the target cysteine. Protein and reversible covalent inhibitor binding can be described by an overall KD. In the presence of free thiols in solution (e.g., GSH) the inhibitor equipped with a double-activated, sterically crowded cyclohexenone-based warhead will “prefer” the protein surface cysteine because of additional (noncovalent) contacts (see panel on the right on top; Kchem refers to the intrinsic activity of the warhead with a free thiol such as GSH). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.