Figure 2 |.
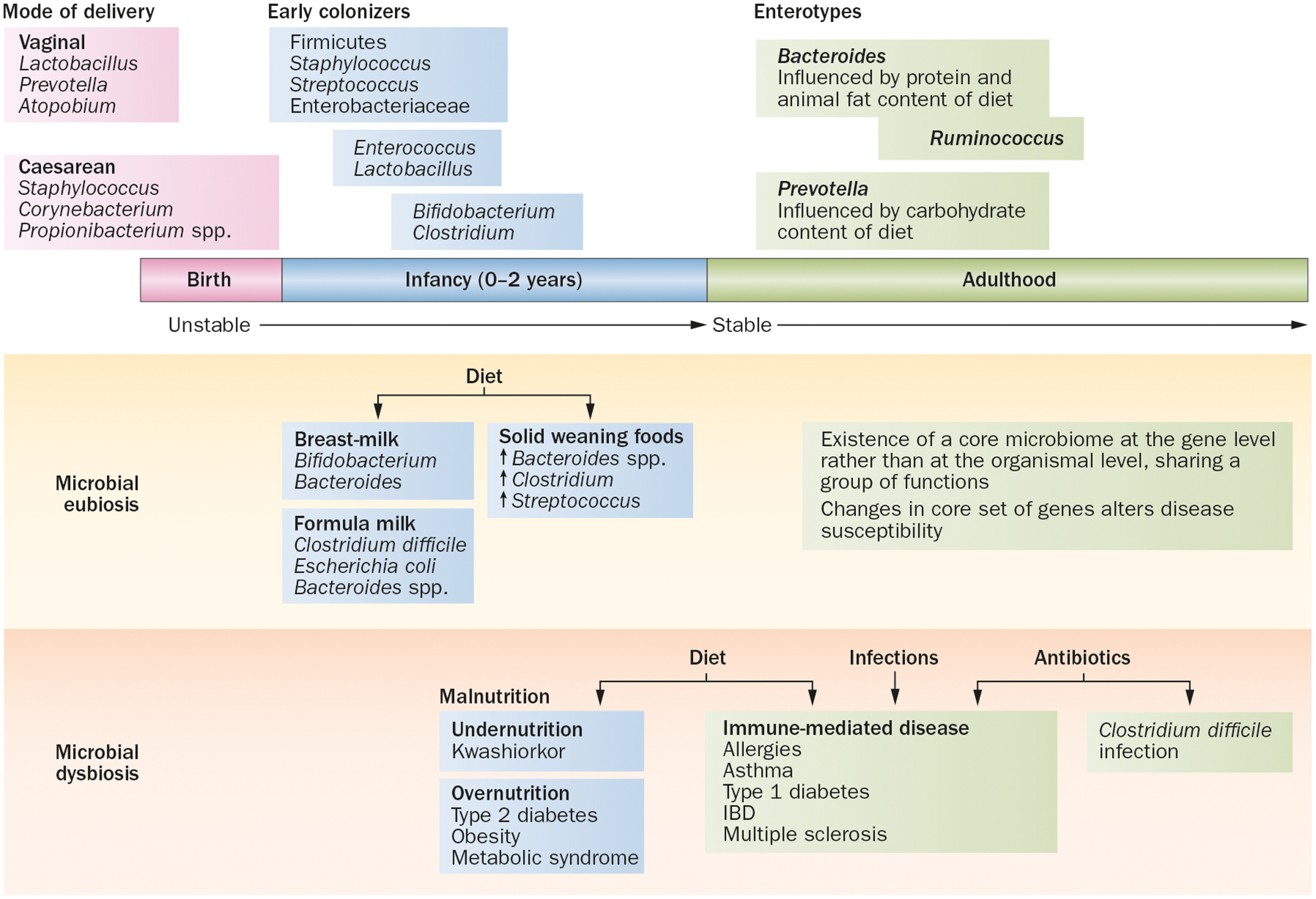
Diet, gut microbiota and dysbiosis. Several features regulate the establishment and composition of the microbiota and their effect on the health and immune function of the host. Eubiosis or a normal microflora structure that protects against infections educates the immune system and contributes to nutrient digestion. Energy harvest is established by early intestinal colonization with specific microbes immediately after birth. An ordered process of subsequent colonization and expansion shaped by diet results in the establishment of distinct ‘enterotypes’, or clusters of microbial communities, that remains fairly stable in adults. Perturbations in the microbial community structure or dysbiosis are induced by factors such as diet, use of antibiotics or infection, which can alter susceptibility to several diseases.
