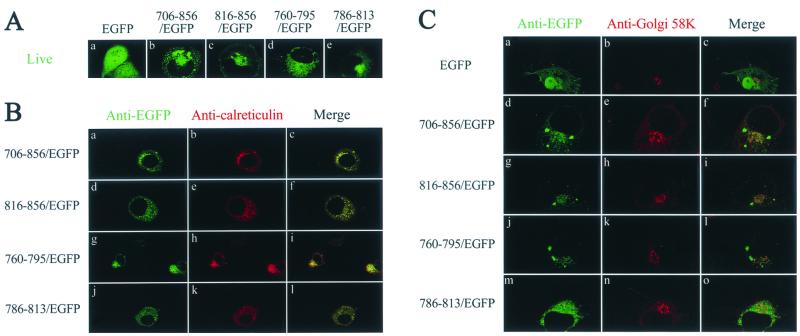
FIG. 9.
Subcellular localization of cytoplasmic tail subdomains fused to the N terminus of EGFP. (A) Examination in a living condition. COS-1 cells were transfected with pEGFP(N2) or a pEGFP(N2) chimera that encoded the cytoplasmic tail or each of the LLP sequences as indicated. One day after transfection cells were directly examined under a confocal microscope. (B) Colocalization with calreticulin. COS-1 cells expressing EGFP or EGFP/LLP fusion proteins were fixed, permeabilized, and successively incubated with rabbit anti-EGFP, FITC-conjugated anti-rabbit immunoglobulin G, goat anti-calreticulin, and TRITC-conjugated anti-goat immunoglobulin G. (C) Localization of EGFP fusion proteins to a compartment distinct from the Golgi apparatus. COS-1 cells expressing EGFP or EGFP/LLP fusion proteins were successively incubated with rabbit anti-EGFP, FITC-conjugated anti-rabbit immunoglobulin G, mouse anti-Golgi 58K, and TRITC-conjugated anti-mouse immunoglobulin G.