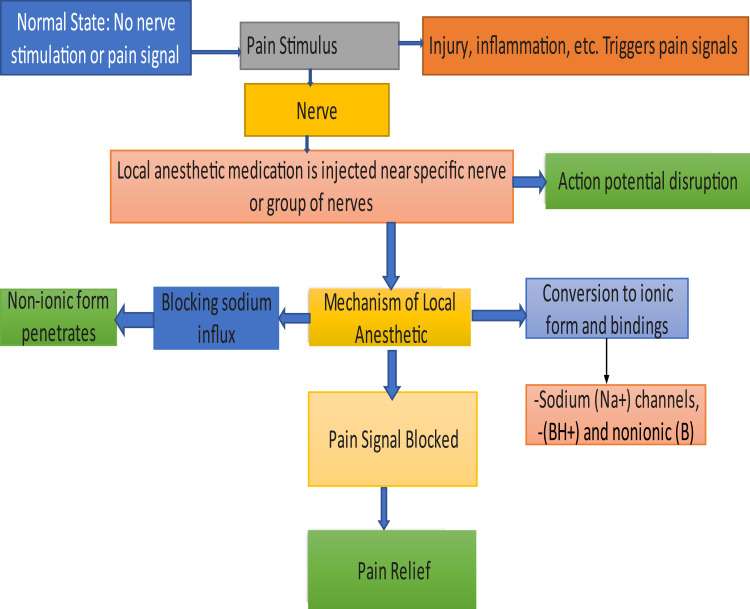
Figure 2.
Mechanism of local anesthetics. This figure illustrates how local anesthetics block pain signals: Normally, no pain signals are transmitted, but injury or inflammation triggers nerve pain. When local anesthetic is injected near the targeted nerves, it disrupts action potentials by blocking sodium (Na+) channels. The anesthetic penetrates in its non-ionic form, converts to an ionic form, and binds to sodium channels, ultimately blocking the transmission of pain signals and providing pain relief.