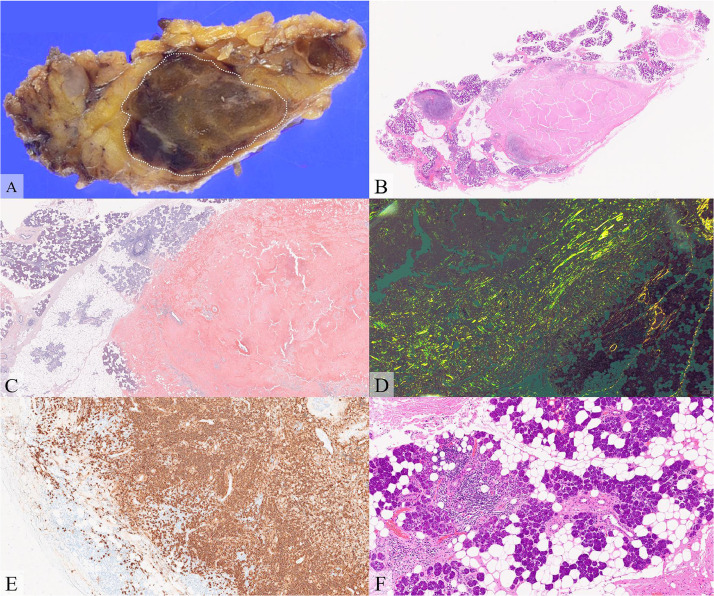
Fig. 2.
Histopathological and immunohistological findings. (A) Formalin-fixed specimen, (B) hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining, (C) direct fast scarlet (DFS) staining, (D) DFS staining under cross-polarized light, (E) CD20 antibody staining, and (F) HE staining.
Gross pathology shows a brownish mass in the resected parotid gland (A, dashed oval). Microscopically, the mass consists of eosinophilic, hyalinized, amorphous material. The eosinophilic amorphous material is positive for DFS staining and shows green birefringence under polarized light microscopy, suggesting amyloid deposits. Lymphocytes and plasma cells at the periphery of the amyloid deposits are positive for CD20 (E). The resected parotid tissue shows stromal fibrosis and fatty replacement, and lymphocytic infiltration around the exocrine glands, suggesting Sjögren syndrome (F).