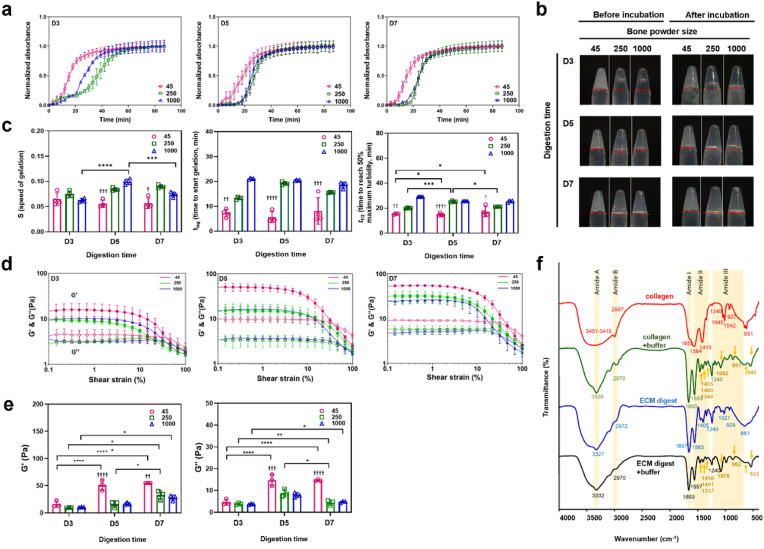
Fig. 3.
Gelation and rheological characterizations of ECM hydrogels from various powder sizes and digestion time. (a) Turbidimetric gelation kinetics of ECM hydrogels. pH-neutralized ECM pepsin digests were added to the wells of a pre-warmed 96-well plate (37 °C), and the absorbance at 405 nm was measured at 3-min intervals (n = 4). The values were normalized between 0 (the initial absorbance) and 1 (the maximum absorbance). (b) Photograph images of each gel after pH neutralization in inverted tubes before and after incubation at 37 °C. The red line indicates the initial volume of the gel before inversion. (c) S (speed of gelation), tlag (time to start gelation), and t1/2 (time to reach 50 % maximum turbidity) were calculated based on turbidimetric curves. (d and e) Storage modulus (G′, open marks) and loss modulus (G″, closed marks) were monitored as hydrogels underwent an amplitude sweep of 0.1–100 % strain at a constant angular frequency. Data represent means ± standard deviation for n = 3. (f) Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) spectra of ECM digest compared with collagen with and without ECM buffer were analyzed. The spectrometer's detection range was 399–4000 cm-1, and the data were measured with an interval of 0.96 cm–1 at room temperature. Statistical significance was determined using a two-way ANOVA test with Tukey's multiple comparisons test (∗p < 0.05 ∗∗p < 0.005 ∗∗∗p < 0.0005∗∗∗∗). The † symbol indicates a significant difference within the groups at the same digestion time). Data represent mean ± SD, N = 4.