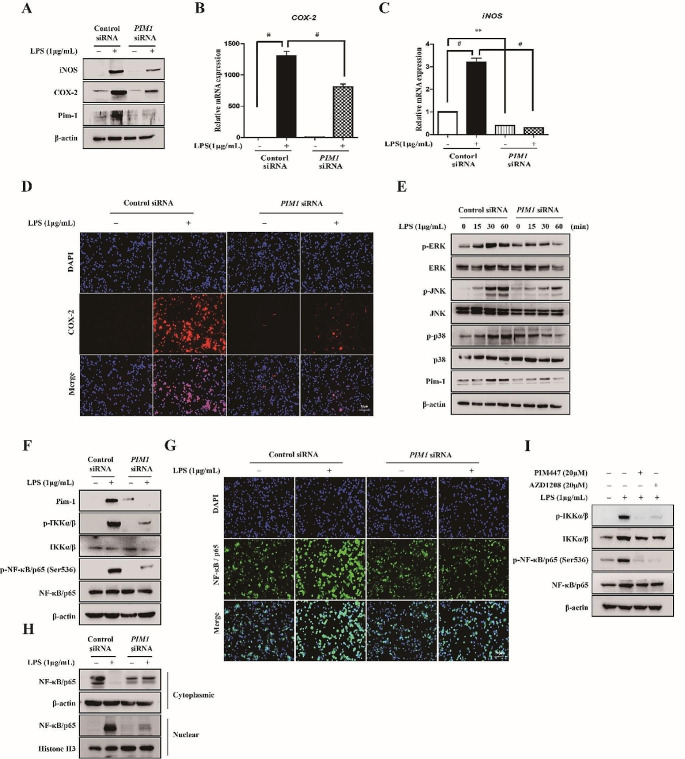
Fig. 3.
The effect of PIM1 knockdown in LPS-induced iNOS, COX-2, MAPKs and NF-κB in macrophage-like THP-1 cells. (A) Whole cell lysates were isolated and used to measure the protein expression levels of iNOS and COX-2 by Western blotting. (B, C) Total RNA was extracted, and used to evaluate the mRNA expression levels of iNOS and COX-2, respectively (** p < 0.01, # p < 0.001). (D) Cells were stained with antibodies to COX-2 (red) and DAPI (blue) and captured at ×200 using fluorescence microscope (scale bar = 50 μm). (E) Cells were stimulated with LPS (1 µg/mL) for the indicated time points. Whole cell lysates were isolated and used to measure the protein expression levels of p-ERK, ERK, p-JNK, JNK, p-p38, and p38 by Western blot analysis. (F) Whole cell lysates were isolated and used to measure the protein expression levels of p-IKKα/β and p-NF-κB p65 by Western blotting. (G) Cells were stained with antibodies to NF-κB p65 (green) and DAPI (blue) and captured at ×200 using fluorescence microscope (scale bar = 50 μm). (H) Cytoplasmic and nuclear proteins were extracted and assayed by Western blot analysis using anti-NF-κB p65 antibody. The expression levels of actin and histone 3 were used as loading controls. (I) THP-1 cells were differentiated into macrophages using 100 nM PMA for 24 h, then the cells were stimulated with LPS (1 µg/mL) for 6 h after pre-treatment with PIM447 (20 µM) and AZD1208 (20 µM) for 1 h. Whole cell lysates were isolated and used to measure the protein expression levels of p-IKKα/β and p-NF-κB p65 by Western blotting