Figure 4. Inhibition of presynaptic PKA blocks MOR-mediated LTD.
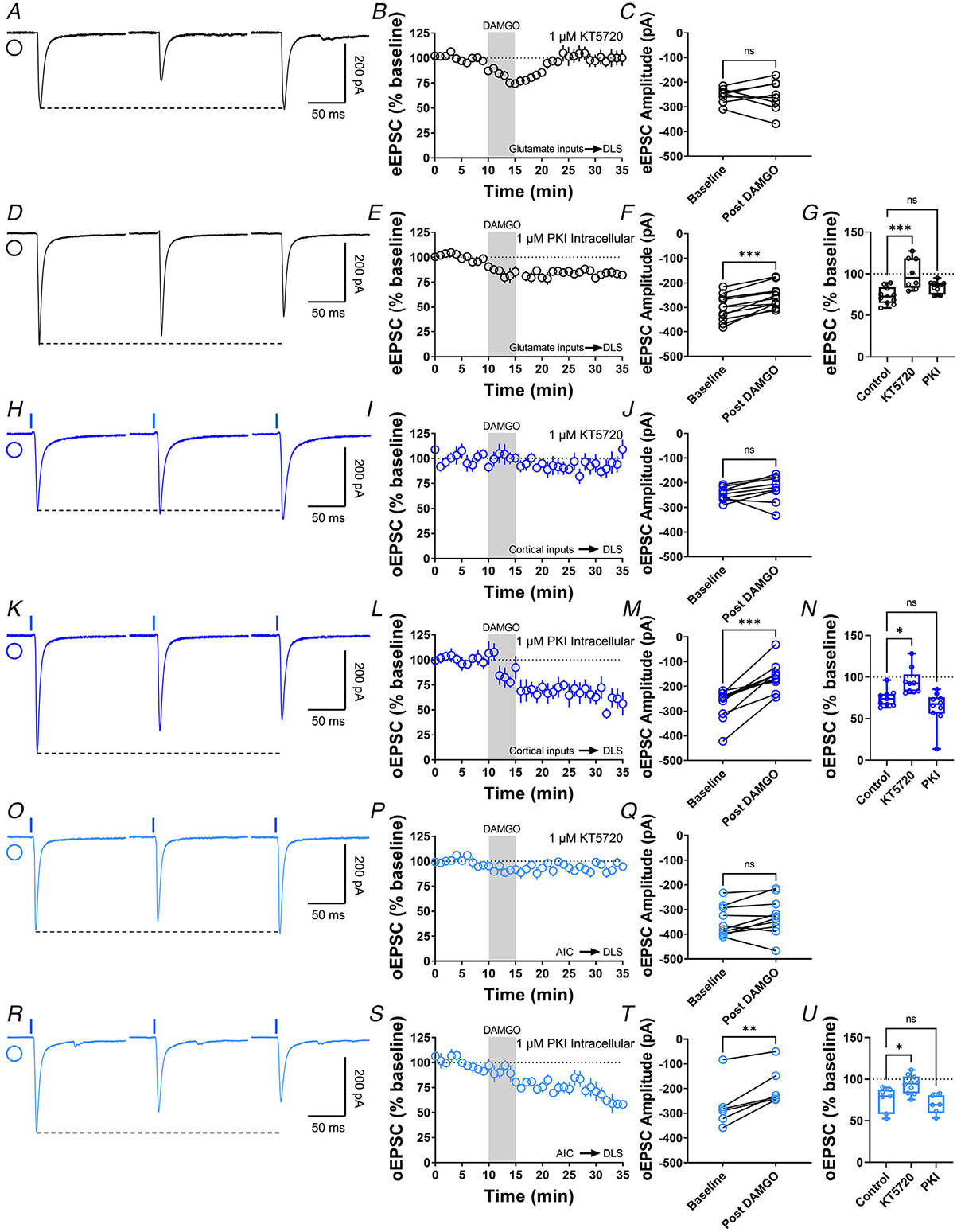
A, representative eEPSC traces showing the effects of DAMGO (0.3 μM, 5 min) application after the preincubation of PKA-selective inhibitor, KT5720 (1 μM, ≥1 hr). B–C, the preincubation of KT5720 blocked glutamatergic MOR-LTD, the eEPSC amplitudes did not change after DAMGO application (0–10 min baseline vs. final 10 min of recording; paired t test, P = 0.865, t7 = 0.176, n = 8 neurons from three mice). D, representative eEPSC traces showing the effects of DAMGO (0.3 μM, 5 min) application after the intracellular dialysis of PKI (1 μM, ≥30 min). E–F, the inhibition of postsynaptic PKA did not alter MOR-LTD. eEPSC amplitudes were reduced after DAMGO application (0–10 min baseline vs. final 10 min of recording; paired t test, P = 0.000120, t10 = 6.07, n = 11 neurons from five mice). G, presynaptic PKA inhibition disrupted MOR-LTD (KT5720: 101 ± 7%, P = 0.000193 vs. PKI: 84 ± 2%, P = 0.121; F(2,26) = 10.65, one-way ANOVA Dunnet’s multiple comparison test). H, representative oEPSC traces showing the effects of DAMGO (0.3 μM, 5 min) application after the preincubation of PKA-selective inhibitor, KT5720 (1 μM, ≥1 h). I–J, PKA inhibition blocked corticostriatal MOR-LTD, with no changes in oEPSC amplitudes after DAMGO application (0–10 min baseline vs. final 10 min of recording; paired t test, P = 0.183, t8 = 1.46, n = 9 neurons from four mice). K, representative oEPSC traces showing the effects of DAMGO (0.3 μM, 5 min) application after the intracellular dialysis of PKI (1 μM, ≥30 min). L–M, the inhibition of postsynaptic PKA did not alter MOR-LTD. oEPSC amplitudes were reduced after DAMGO application (0–10 min baseline vs. final 10 min of recording; paired t test, P = 0.000118, t9 = 6.45, n = 10 neurons from four mice). N, presynaptic PKA inhibition disrupted cortical MOR-LTD (KT5720: 94 ± 5%, P = 0.0305 vs. PKI: 64 ± 6%, P = 0.235; F(2,25) = 8.805, One-way ANOVA Dunnet’s multiple comparison test). O, representative AIC-DLS oEPSC traces showing the effects of DAMGO (0.3 μM, 5 min) application after the preincubation of PKA-selective inhibitor, KT5720 (1 μM, ≥1 h). P–Q, KT5720 blocked AIC-expressed MOR-LTD, with no changes in oEPSC amplitudes after DAMGO application (0–10 min baseline vs. final 10 min of recording; paired t test, P = 0.141, t9 = 1.613, n = 10 neurons from three mice). R, representative AIC-DLS oEPSC traces showing the effects of DAMGO (0.3 μM, 5 min) application after the intracellular dialysis of PKI (1 μM, ≥30 min). S–T, postsynaptic PKA inhibition did not alter specific AIC MOR-mediated LTD. oEPSC amplitudes were reduced after DAMGO application (0–10 min baseline vs. final 10 min of recording; paired t test, P = 0.00488, t5 = 4.8, n = 6 neurons from three mice). U, presynaptic PKA inhibition disrupted AIC MOR-LTD (KT5720: 94 ± 4%, P = 0.0171 vs. PKI: 69 ± 5%, P = 0.518; F(2,20) = 8.411, one-way ANOVA Dunnet’s multiple comparison test). Time course data represent means ± SEM. Box plots show average of the final 10 min of recording and represent median and interquartile ranges. ns = not significant, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
