Figure 5. Postsynaptic PKA is required for CA1 hippocampal LTP.
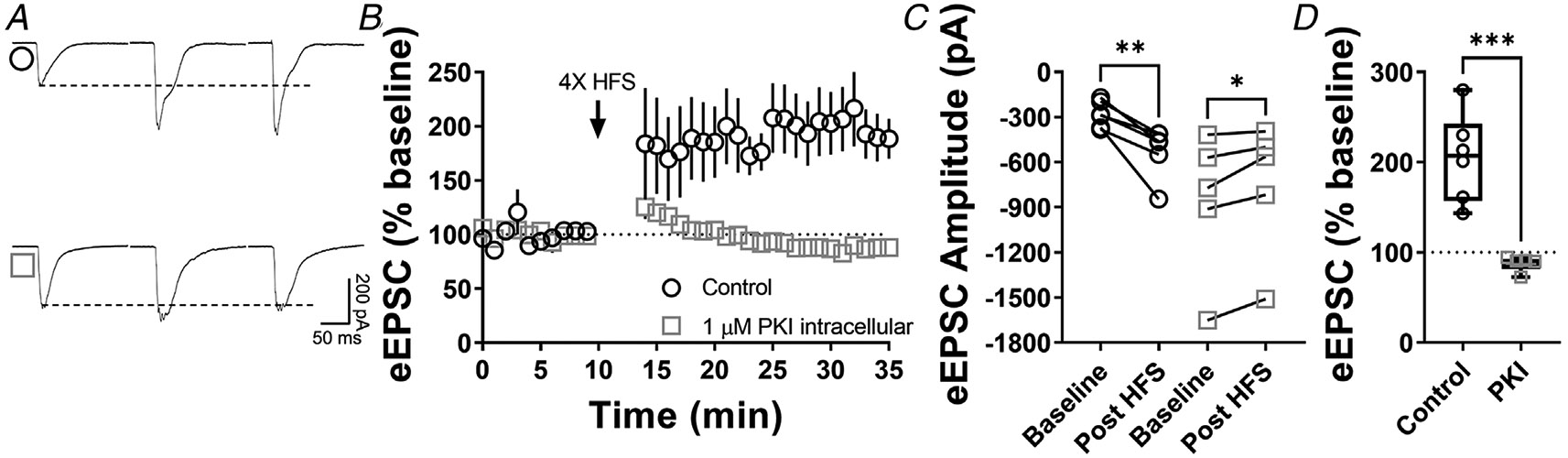
A, representative eEPSC traces before and after high-frequency stimulation (HFS) (four pulses of 100 Hz, 1 min inter-pulse interval), showing the effects of PKI (1 μM) intracellular diffusion into CA1 pyramidal neurons within hippocampal brain slices of C57BL/6J mice. B–C, postsynaptic PKA signalling is necessary to the induction of LTP in CA1 (0–10 min baseline vs. final 10 min of recording; Control: paired t test, P = 0.00587, t5 = 4.6, n = 6 neurons from four mice; PKI: paired t test, P = 0.0282, t4 = 3.36, n = 5 neurons from four mice). D, box plot shows the average disruption of hippocampal LTP by inhibiting postsynaptic PKA (Control: 205 ± 49 % vs. PKI: 88 ± 9%, P = 0.000551, t9 = 5.22, unpaired t test). Time course data represent means ± SEM. Box plots represent median and interquartile ranges. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
