Figure 1. Cryo-EM structures of the human Sec61 complex inhibited by various small-molecule inhibitors.
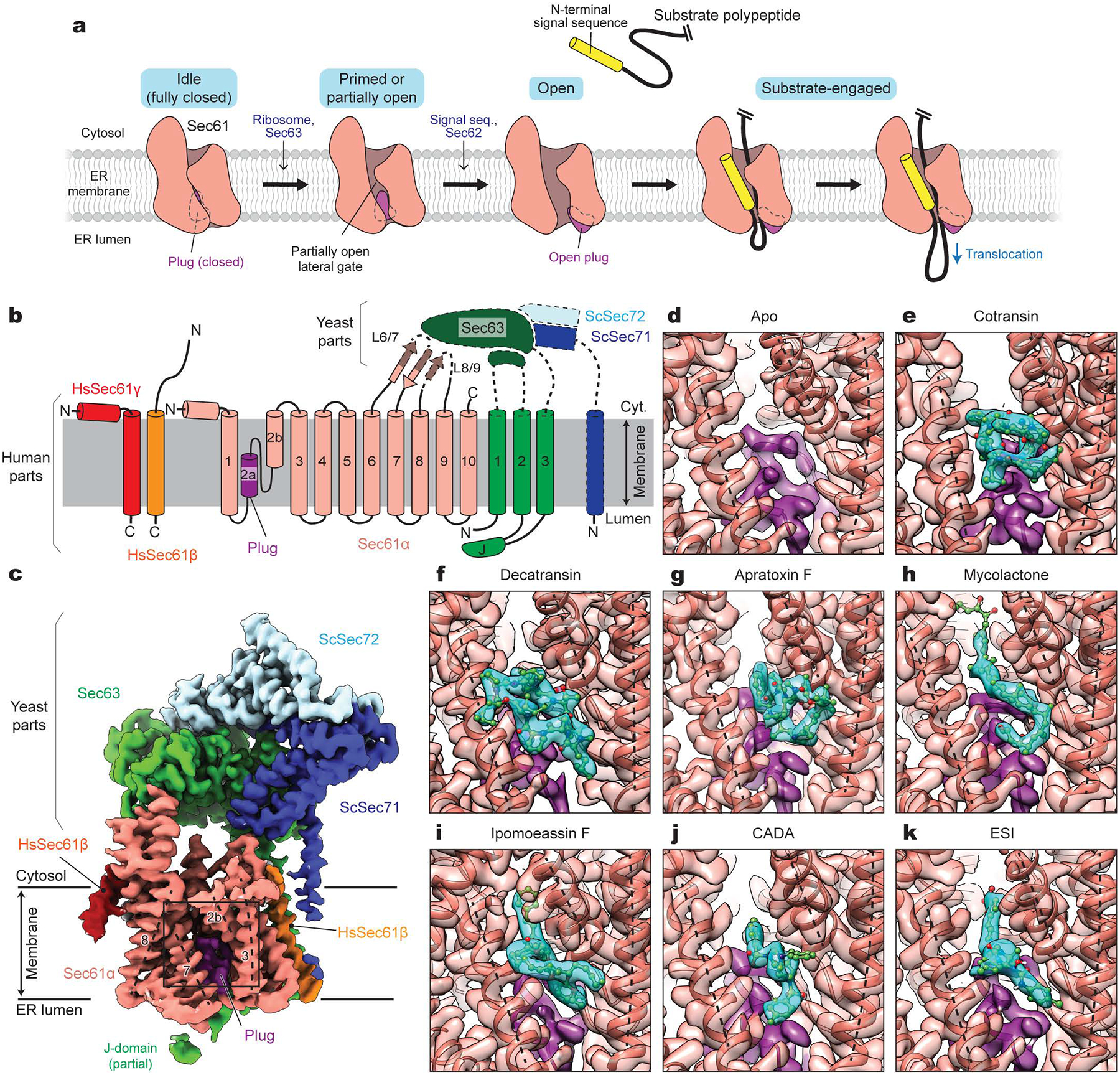
a, Architecture of the Sec61 channel and overall model for gating and substrate engagement. b, Design of a human-yeast chimeric Sec complex. Parts derived from human and yeast proteins are outlined with solid and dashed lines, respectively. Note that except for the cytosolic L6/7 and L8/9 loops, Sec61α is from the human SEC61A1 protein sequence. Hs, Homo sapiens; Sc, Saccharomyces cerevisiae; J, J-domain. c, 2.7-Å-resolution cryo-EM map of the chimeric Sec complex in an apo state (Class 1, unsharpened map). The lateral gate helices are indicated by dashed lines and TM numbers. The region outlined by a rectangle indicates the inhibitor-binding site (also see d–k). d–k, Views into the inhibitor-binding site of Sec61α of apo and inhibitor-bound structures. Cryo-EM maps (semi-transparent surface) and atomic models were overlaid. Inhibitor and plug densities are shown in cyan and purple, respectively. Dashed lines indicate lateral gate helices TMs 2b, 3, and 7 as in c.
