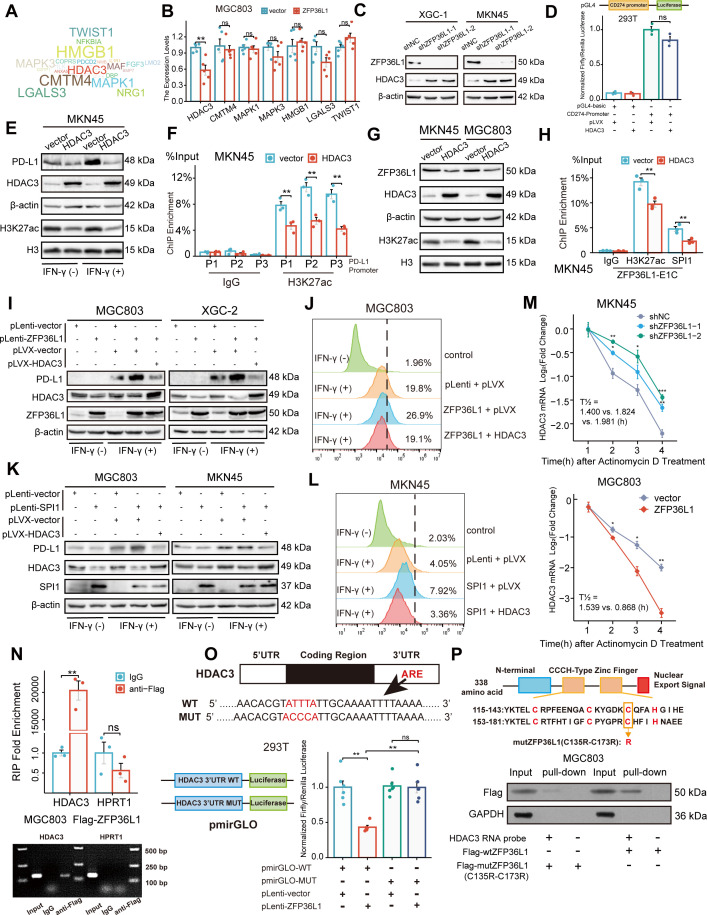
Figure 5. ZFP36L1 positively regulates PD-L1 by activating HDAC3 mRNA decay.
(A) Word cloud of predicted ZFP36L1 target genes. (B) The mRNA expression of predicted target genes in MGC803 cell overexpressing ZFP36L1 (n=5). (C) HDAC3 protein expression in ZFP36L1 knockdown cells. (D) Effect of HDAC3 on CD274 promoter activity in 293T using dual-luciferase assay (n=3). (E) Correlation between changes of histone H3K27 acetylation and PD-L1 protein expression in MKN45 cells overexpressing HDAC3. (F) Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay showing the histone H3K27 acetylation levels of CD274 promoter regions in MKN45 cells overexpressing HDAC3 (n=3). (G) Correlation between changes of histone H3K27 acetylation and ZFP36L1 protein expression. (H) The H3K27ac and SPI1 enrichment of ZFP36L1-E1C regions using ChIP assay (n=3). (I, J) PD-L1 protein expression in simultaneous ZFP36L1 and HDAC3 overexpression cells. (M) HDAC3 mRNA decay in ZFP36L1 knockdown and overexpression cells after actinomycin D treatment. (N) ZFP36L1 mRNA-binding level by RNA-binding protein immunoprecipitation (n=3). (O) ZFP36L1 mRNA-binding site in AU-rich element (ARE) of 3ʹUTR confirmed using dual-luciferase assay (n=6). (P) CCCH-type zinc finger domain of ZFP36L1 protein binding to HDAC3 mRNA confirmed using RNA pull-down assay. ARE, adenylate uridylate- (AU-) rich element; 3ʹUTR, 3ʹ untranslated region. ***, p<0.001; **, p<0.01; *, p<0.05; ns, p≥0.05. (B, F) Wilcoxon rank sum test, (D) one-way ANOVA post hoc Tukey HSD test, (H) t-test, (N) Welch’s t-test, and (O) Kruskal-Wallis with Dunn’s test were used for statistical analysis.