Figure 3.
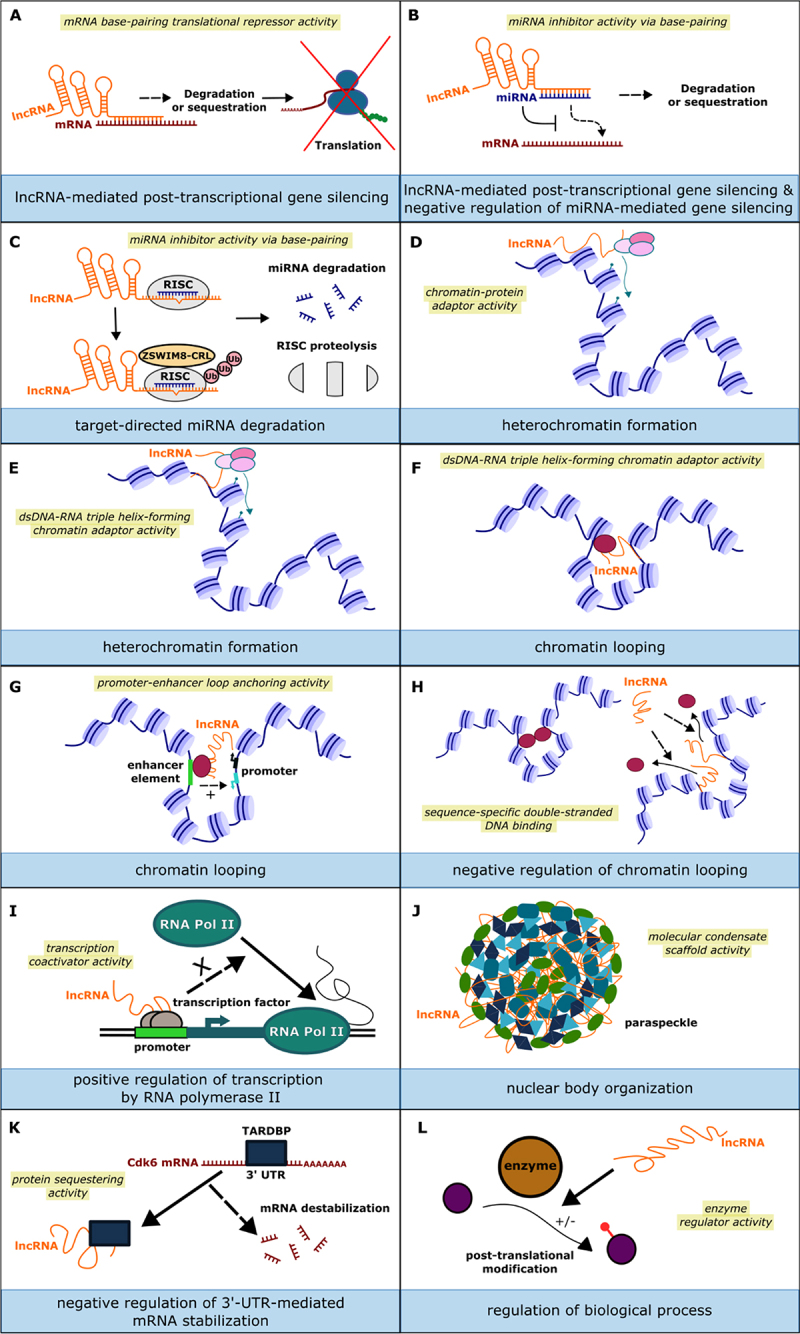
The diversity of lncRNA activities. Each panel depicts an activity that has been described for a lncRNA to accompany examples in the main text. The recommended MF term (or parent term) is highlighted in yellow and the BP term (or parent term) is shown in the bottom blue strip. LncRNAs can act post-transcriptionally to down-regulate mRNAs (A) or miRNAs (B) in the cytosol. (C) Target-directed miRNA degradation involves the RISC. It is not limited to lncRNAs and should therefore be co-annotated with ‘lncRNA-mediated post-transcriptional gene silencing’ (GO:0000512). (D-G) in the nucleus, lncRNAs can act as adaptor molecules to bring components together to influence chromatin structure. Some lncRNAs bind genomic DNA to recruit proteins (E,F) or to displace DNA-binding proteins (H). Other types of ‘molecular adaptor activity’ (GO:0060090) performed by lncRNAs include acting as transcriptional co-regulators (I) and assembling non-membrane bound organelles (J). LncRNAs have also been shown to sequester proteins, such as with the binding of TARDBP by the lncRNA Gadd7 (K) or inhibit enzymes (L). In the examples shown in this figure, many MFs can be annotated using terms from the ‘molecular adaptor activity’ (GO:0060090) branch of the GO and take part in BPs from the ‘cellular component organization’ (GO:0016043) branch. These terms are shown in the GO hierarchy in Figure S1B and Figure S1D, respectively.
