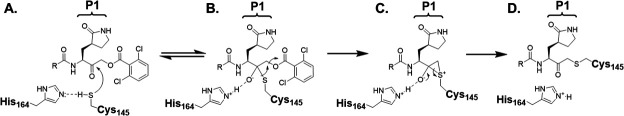
Fig 2.
The mechanism of irreversible inhibition of cysteine proteases by acyloxymethyl ketones. (A) The active site His164 acts as a base to enhance the nucleophilicity of the Cys145 thiol. (B) Nucleophilic attack of the Cys145 thiol to the ketone carbonyl generates a reversible thiohemiketal complex. (C) Attack by the thiol leads to the thiiranium intermediate species, which collapses to form the irreversible covalent thiol adduct (D).