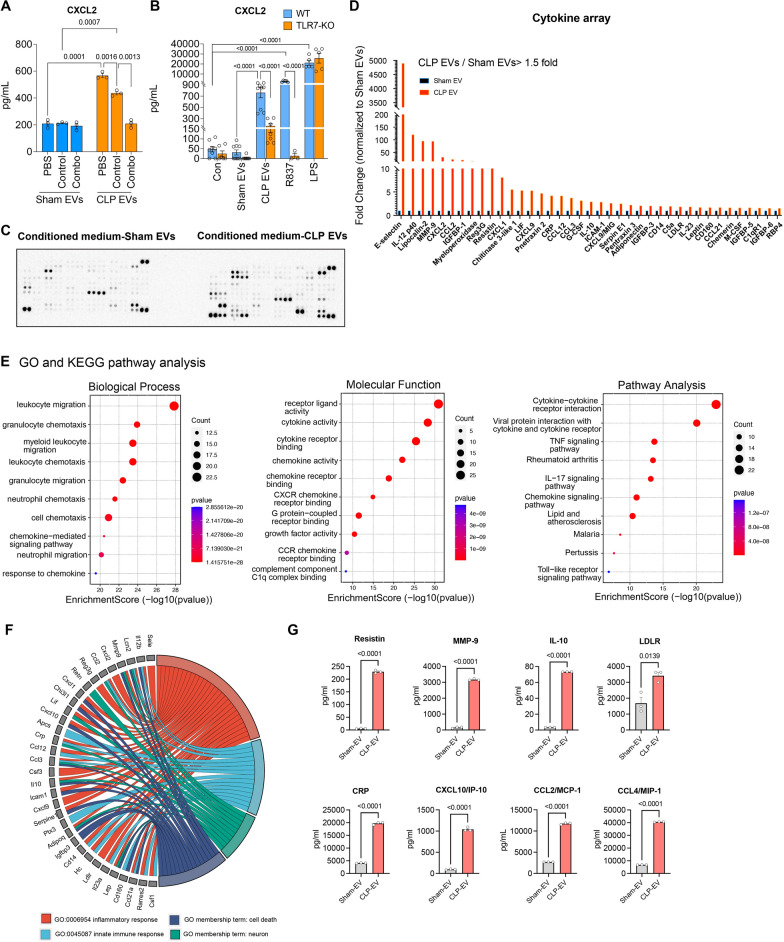
Fig. 6.
CLP EVs-mediated microglial activation is partially attributed to miRNAs and TLR7 signaling. A Anti-miRs combo (anti-miR-146a, -122, -34a, -145a, 200 nM) paritially attenuated CLP EVs-mediated CXCL2 production in the microglia. Prior to applying to microglia culture, sham EVs and CLP EVs (2.5 × 109 particles/mL) were treated with PBS, control oligonucleotide,or anti-miR combination (combo) at a concentration of 200 nM, including anti-miR-146a, -34a, -miR-122, and miR-145a, for 1 h. Microglial media were then collected 24 h after treatment and assayed for CXCL2 using ELISA. Each bar represents triplicate samples with each experiment repeated twice. n = 3/group B. Plasma EVs from septic mice induce CXCL2 production in part via TLR7 signaling. Cultured microglia from WT and TLR7 KO mice were treated with sham EVs (2.5 × 109 particles/mL), CLP EVs (2.5 × 109 particles/mL), R837 (100 ng/mL), and LPS (50 ng/mL) for 24 h. The supernatant was then collected for CXCL2 analysis using ELISA. n = 3–9/group. Immune blot (C) and quantification of integrated intensity (D) of cytokine array in the conditioned media from EVs-treated microglia. E Enrichment analysis of GO-biological process, molecular function, and KEGG pathway. F GO chord diagram reflects the differential gene expression (shown on the left) and enriched functional categories (shown on the right) including inflammatory response, innate immune response, cell death, and neurons. G Luminex analysis valiated several upregulated molecules in the conditioned media identified from cytokine array and pathway enrichment analysis including Resistin, MMP-9, IL-10, LDLR, CRP, CXCL10, CCL2, and CCL4. n = 3/group