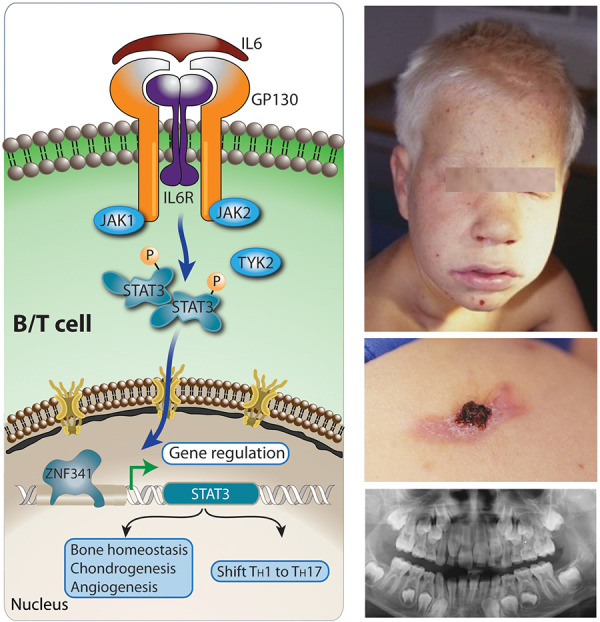
Figure 6. Physiology of STAT3 signaling (left panel) and a 7-year-old boy with coarse facial features (right panel, above), eczema, cold skin abscesses (middle) and delayed dentition at 10 years of age (below, different patient). IL6 signals through the IL6RST (signal transducer of IL6 receptor complex), composed of glycoprotein 130 (GP130) and the IL6R. Other cytokines of the IL6 cytokine family utilize GP130 encoded by IL6ST (IL11, OSM, LIF, CNTF, CT-1, CLCF1, IL27, IL35, and IL39). IL6 then activates through JAK-STAT signal transduction the zinc finger protein 341 (ZNF341) TF, which promotes STAT3 transcription. IL6 and IL23 activate STAT3, which turns on RORC, encoding RORγt the master regulator for a TH1/TH17 T-cell response shift as well as chondrogenesis, bone repair, angiogenesis/vascularization (induction of vascular endothelial factor 3 (VEGF3)) [23]. The phosphoglucomutase 3 (PGM3) (not shown in figure) enzyme catalyzing the isomerization of N-acetyl-glucosamine-6-phosphate to N-acetyl-glucosamine-1-phosphate during the generation of UDP-N-acetyl-glucosamine UDP-GlcNAc. During glycosylation, sugar chains are added to either proteins or lipids, using basic sugar building blocks (UDP-GlcNAcs) to make N-glycans, O-glycans, proteoglycans, and glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored proteins all participating in cell signaling.