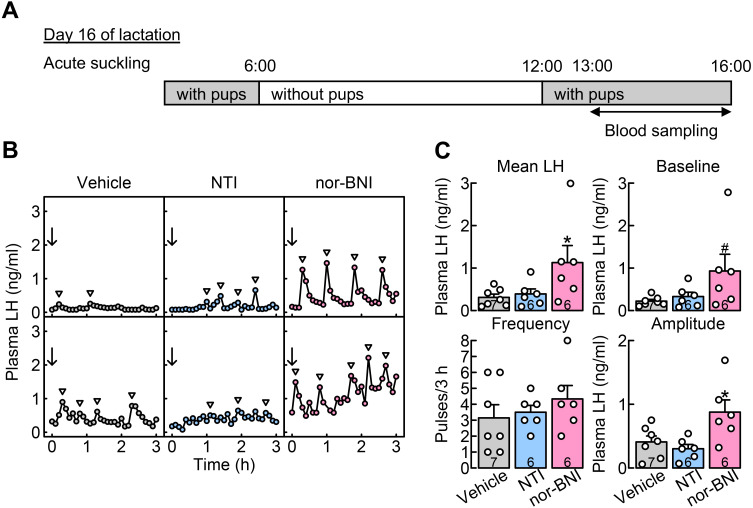
Fig. 5.
Central administration of nor-binaltorphimine (nor-BNI, a selective κ opioid receptor (KOR) antagonist), but not NTI (a selective DOR antagonist) blocked the suppression of LH secretion in OVX + E2 lactating rats with acute suckling stimuli during late lactation. (A) Schematic illustration of experimental schedule: Blood samples were collected from free-moving conscious rats in the acute suckling group, in which animals received their pups for 1 h after the 6-h pup removal period immediately before blood sampling on day 16 of lactation. (B) Plasma LH profiles of representative OVX + E2 lactating rats administered with NTI, nor-BNI, or vehicle on day 16 of lactation. Blood samples were collected every 6 min for 3 h. Immediately after the first blood collection, NTI, nor-BNI, or vehicle (arrows) was injected into the 3V. Arrowheads indicate the peaks of LH pulses identified by the PULSAR computer program. (C) The mean LH concentrations and the amplitude of LH pulses were significantly higher in nor-BNI-injected rats than in vehicle-injected rats with acute suckling stimuli on day 16 of lactation (*, P < 0.05, one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test). In addition, the baseline of LH pulses tended to be higher in nor-BNI-injected rats than in vehicle-injected control rats (#, P = 0.068, one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test). No significant difference was observed in the frequency of LH pulses between nor-BNI- and vehicle-injected lactating rats. Besides, no significant differences were observed in the mean LH concentrations and the baseline, frequency, and amplitude of LH pulses between the NTI- and vehicle-injected dams. Values in bar charts are means ± SEMs. Open circles on the bar chart indicate the individual values. The number in each column indicates the number of animals used.