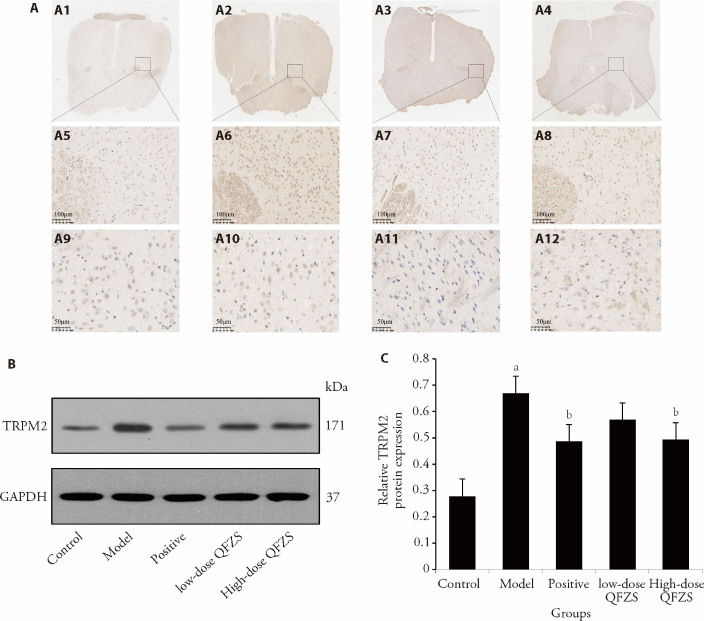
Figure 2. Effects of QFZS on TRPM2 expression.
A: the immunohistochemistry staining of TRPM2, A1-A4: images of control (A1), model (A2), Lose-dose QFZS (A3), High-dose QFZS(A4) (× 1); A5-A8: images of control (A5), model (A6), Lose-dose QFZS (A7), High-dose QFZS(A8) (× 200, bar = 100 μm); A9-A12: images of control (A9), model (A10), Lose-dose QFZS (A11), High-dose QFZS(A12) (× 400, bar = 50 μm). B: Western blotting representative images of TRPM2 respective quantification in the hypothalamus; C: protein expression levels of TRPM2. Control group: sham operated; Model group: Yeast-induced fever model without treatment; Positive group: Yeast-induced fever model with Aspirin (100 mg/kg); Lose-dose QFZS group: Yeast-induced fever model with low-dose QFZS (2.82 g/kg); High-dose QFZS group: Yeast-induced fever model with high-dose QFZS (5.64 g/kg). TRPM2: transient receptor potential melastatin 2; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; QFZS: Qingfei Zhisou oral liquid. Data represent the mean ± standard deviation using one-way analysis of variance (n = 5). Compared with the sham group, aP < 0.05; compared with the model group, bP < 0.05.