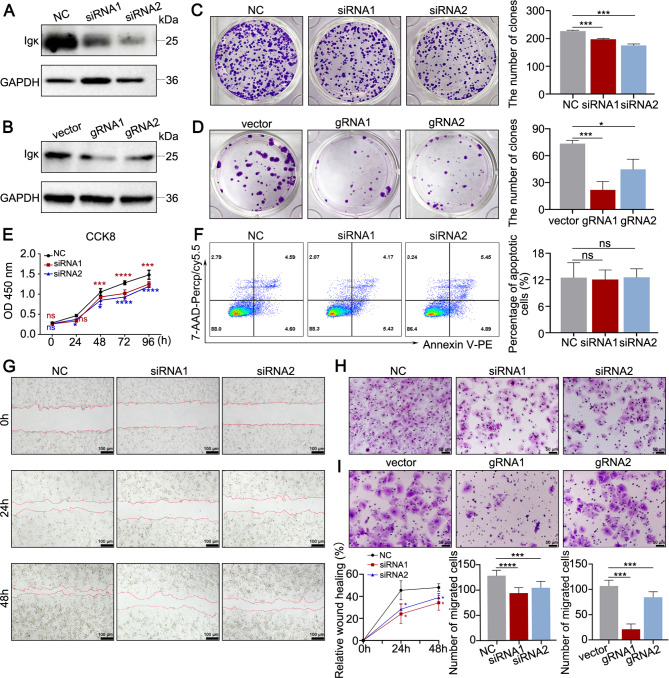
Fig. 2.
Hepatocyte-derived Igκ promotes the proliferation and migration of HCC cells. A - B Western blot analysis of Igκ protein levels in Huh7 cells was performed to detect the effect of Igκ knockdown by siRNA or Igκ knockout by the CRISPR-Cas9 system. C - D A colony formation assay was conducted to detect the proliferation capacity of Huh7 cells after the knockdown (C) or knockout (D) of Igκ (middle). The quantification of the number of colonies is shown (right) (n = 3). E A CCK-8 assay was performed to detect the proliferative capacity of Huh7 cells at different time points after Igκ was knocked down (n = 3). F Representative plots and quantification of apoptotic Huh7 cells after the knockdown of Igκ via flow cytometric analysis (n = 3). G - I Wound healing assays (G) and transwell migration assays (H - I) were used to detect the migration ability of Huh7 cells in which Igκ was knocked down by using siRNA or knocked out by using Igκ gRNA. The quantification of the relative wound healing area and migrated cell counts are shown (lower right) (n = 3). Scale bar, 100 μm (left), 50 μm (right). The data are presented as the mean ± SD. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001, and ns, not significant