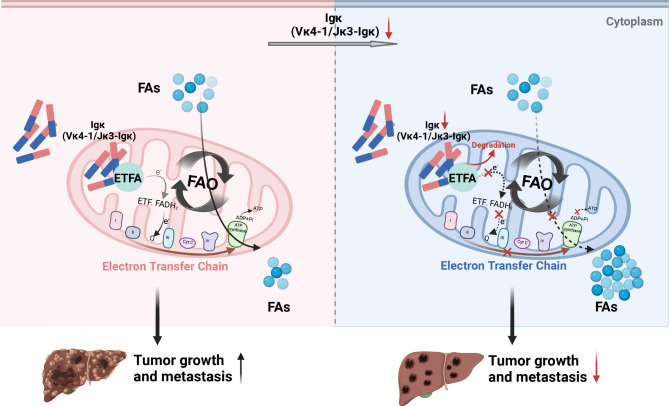
Fig. 8.
A working model explaining how hepatocyte-derived Igκ promotes HCC progression by stabilizing ETFA to facilitate fatty acid β-oxidation. Hepatocyte-derived Vκ4-1/Jκ3-Igκ interacts with the electron transporter ETFA on the mitochondrial respiratory chain, and loss of Igκ promotes ETFA protein degradation, leading to decreased expression of mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes III and IV, thereby causing aberrant FAO and lipid accumulation. Dysregulated lipid metabolism subsequently inhibits the proliferation and migration of HCC cells, thereby delaying HCC development