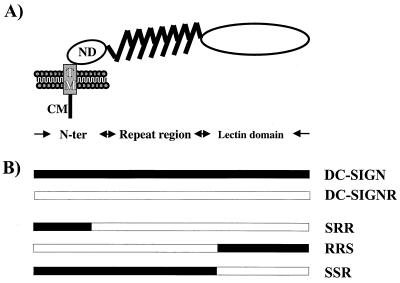
FIG. 1.
Schematic representation of DC-SIGN and the DC-SIGN/DC-SIGNR chimeras analyzed. (A) Domain structure of DC-SIGN as identified by sequence analysis. DC-SIGNR exhibits a comparable domain organization. N-ter, N terminus; CM, cytoplasmic domain; TM, transmembrane domain; ND, N-terminal domain. (B) Schematic structure of the DC-SIGN/DC-SIGNR chimeras. DC-SIGN/DC-SIGNR chimeras were generated by fusing the N terminus of DC-SIGN to the DC-SIGNR backbone (chimera SRR) and by exchanging the lectin domains of both proteins (chimeras RRS and SSR). For detection of protein expression, all constructs were engineered to contain a C-terminal, antigenic AU-1 tag.