Figure 1.
Identification of 1280 bona fide somatic mosaic variants in human DRG and SG from 3 neurotypical control donors.
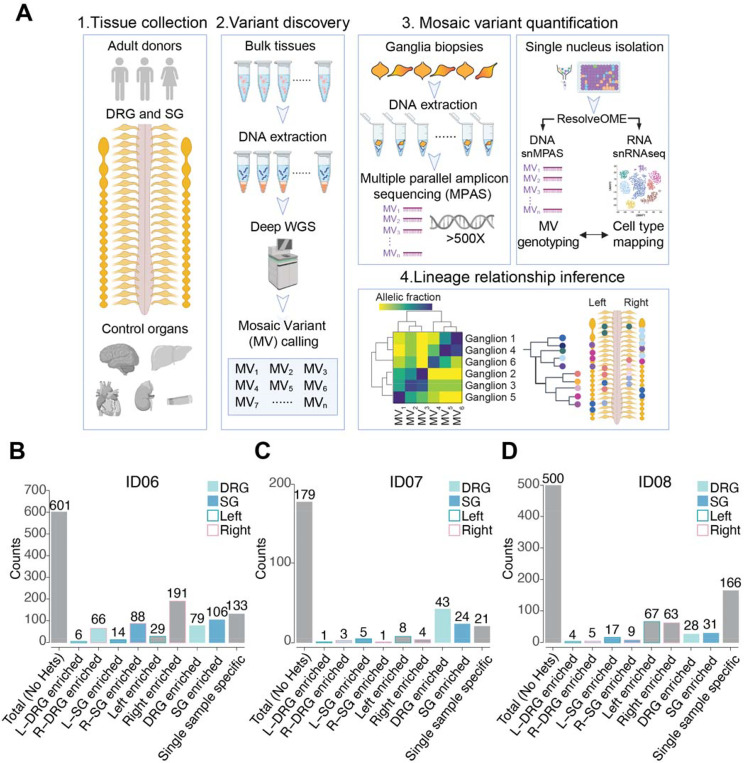
(A) Strategy to deconvolve lineage of sensory (DRG) and sympathetic ganglia (SG): (1) Tissue collection: DRG and SG dissected from 2 male and 1 female donors. Other major organs were also collected to infer clonal relationship; (2) Variant discovery: 300x and 30x whole-genome sequencing (WGS) of bulk peripheral organs and ganglia biopsies respectively, followed by best-practice mosaic variant (MV) calling pipelines, identified candidate MVs. (3) Candidate MVs quantified in dissected tissues or single nuclei isolated from individual ganglia by multiple parallel amplicon sequencing (MPAS) or single-nucleus MPAS (snMPAS) respectively. (4) Lineage tree inference: Variant allelic fractions of validated MVs in individual ganglia analyzed and anatomically mapped. Lineage relationships of ganglia deconvolved by computing clonal similarities between samples and statistical modeling of clonal dynamics. DRG, dorsal root ganglia; SG, sympathetic ganglia.
(B-D) Mosaic variant counts identified from donors ID06 (B), ID07 (C), and ID08 (D), classified by tissue and anatomical distribution. Variant detected 1.5x more frequent in a group is defined as enriched. See STAR methods for mathematical quantification. Heterozygous variants (Hets) were excluded. L, left; R, right.