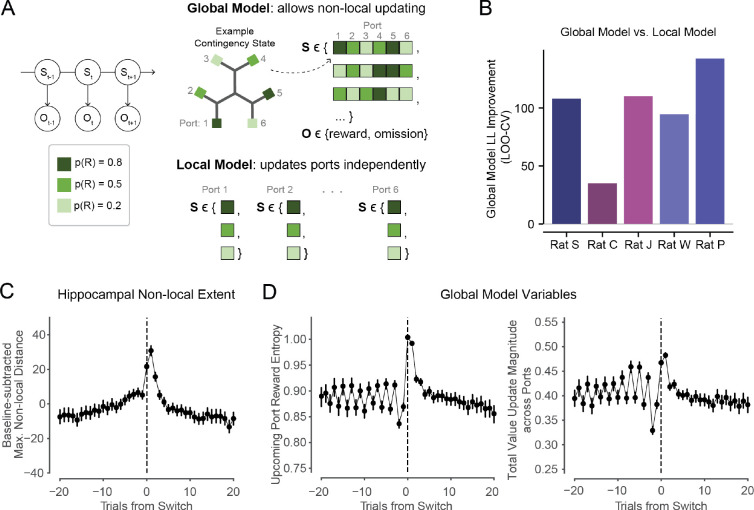
Figure 5. Behavioral modeling captures enhanced learning opportunities in early patch experience.
(A) Left: schematic of Hidden Markov Model with hidden state S and observation O on each trial t. Colors correspond to potential nominal reward probabilities. Upper right: schematic of Global Model, showing example contingency states S with specific values for each port, and the two potential observations O of reward outcomes on each trial at the chosen port. Lower right: Example states S in Local Model, in which each port’s value is estimated independently. The Global and Local models had matched reward distributions, though here we visualize unique example states.
(B) Leave-one-out cross-validated log-likelihood improvement (higher is better) of Global Model versus Local Model. Global Model better fit behavior in all animals (p=.0035, .0285, .0006, .0013, .0104, t-test on cross-validated log-likelihoods per day).
(C) All animals’ normalized maximum hippocampal non-local distance represented on trials leading up to and following Switch trials, for non-local representations both ahead and behind (as in Fig. 4D,G). Trial-level quantification, rather than sub-trial-level quantification, shown here to match trial-level resolution of behavioral model. Error bars are 95% CIs on the mean.
(D) Global Model variables related to learning opportunities in new patch and associated value updating across the maze are enhanced upon patch Switching. Left: Entropy over reward states at upcoming reward port shows asymmetrical pattern around Switch trials, becoming elevated on and after Switch trials, and decreasing across trials thereafter. Patterns were consistent across animals, shown individually in Fig. S5D. Right: Absolute value update resulting from each trial’s reward outcome, summed across all ports in maze. Degree of value updating is elevated upon patch Switching, and decreases across trials the longer the animal Stays within a patch. Patterns are similar for updates both within the current patch and across unoccupied patches (shown individually in Fig. S5). Error bars are 95% CIs on the mean. Patterns were consistent across animals, shown individually in Fig. S5E.