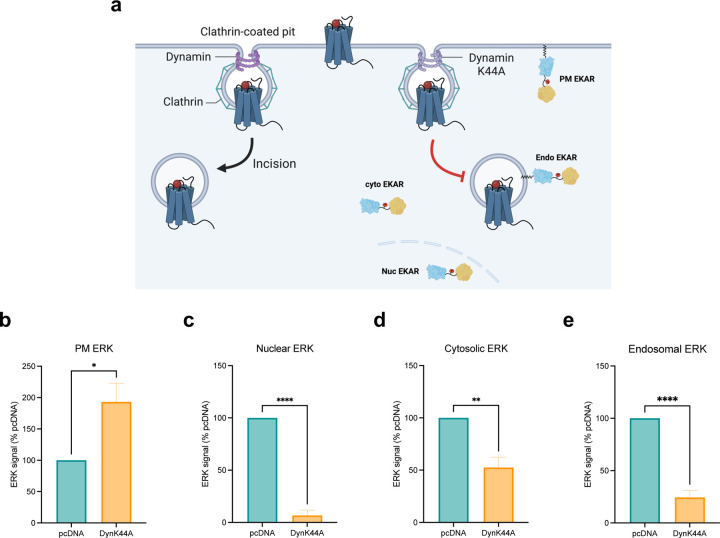
Figure 5: Endocytosis is essential for regulating ERK signaling in subcellular locations.
(a) Schematic of EKAR BRET assay with or without endocytosis inhibition. Cells were transfected with FLAG-AT1R, EKAR biosensors, and dynamin K44A to inhibit receptor internalization or pcDNA 3.1 as control. (b-e) AUC quantification of ERK activity in early endosomes, nucleus, cytosol, and PM with endocytosis inhibition. Cells were stimulated with 1 μM AngII for 5 min (PM ERK) or 30 min (nuclear, cytosolic, endosomal ERK). Data was normalized to AngII-stimulated pcDNA condition as 100% and is shown as mean ± SEM of n independent biological replicates, n=4 for PM and cytosolic ERK, n=5 for nuclear and endosomal ERK. Statistical analysis was performed using unpaired two-tailed t-tests to compare pcDNA vs. dynamin K44A. *P<0.05; **P<0.005; ****P<0.0001.