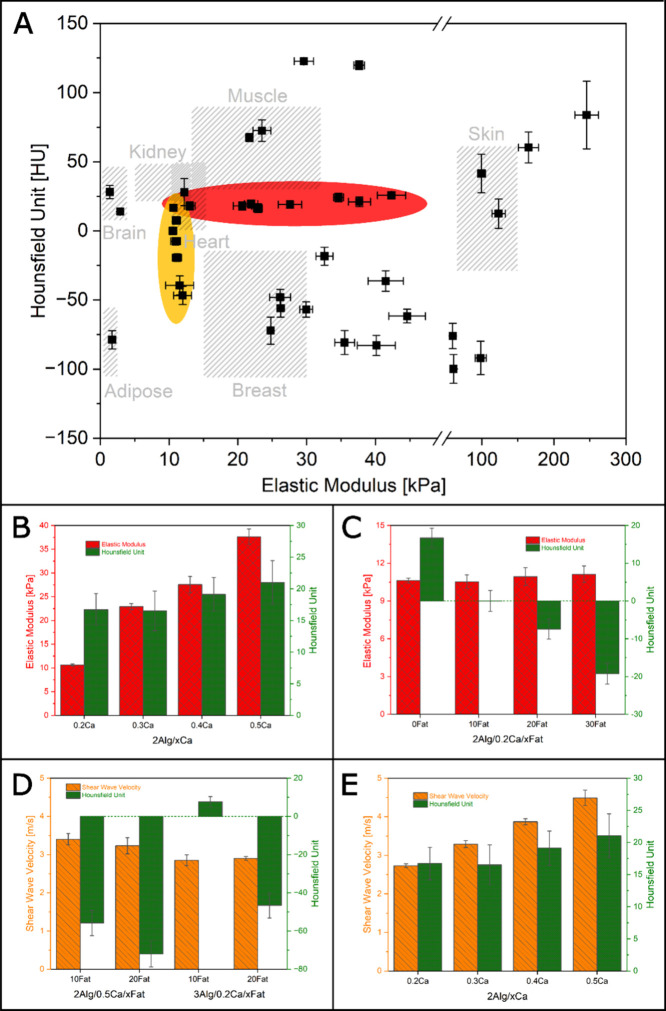
Figure 2.
(A) The HU, elastic modulus, and their corresponding standard deviation of different material variations, showing the influence of concentration and cross-linking degree of alginate and fat addition on the elastic modulus and CT attenuation (HU). An increase in the concentration of cross-linker (Ca2+) results in a significant increase in the elastic modulus, while having no significant effect on the CT attenuation in HU (grouped in red circle). The addition of coconut fat significantly decreases the CT attenuation in HU while the elastic modulus is not affected (grouped in the yellow circle). A wide range of elastic modulus and CT attenuation can be achieved even beyond the real organs or tissues by adjusting the concentration of alginate, degree of cross-linking, and the addition of coconut fat. The Hounsfield unit and elastic modulus of human tissue and organs were obtained from the previous studies.18−24 (B) Influence of cross-linking degree and (C) fat addition on the elastic modulus and CT attenuation. (D,E) Influence of alginate concentration, cross-linking degree, and fat addition on the CT attenuation and shear wave velocity of material variations.