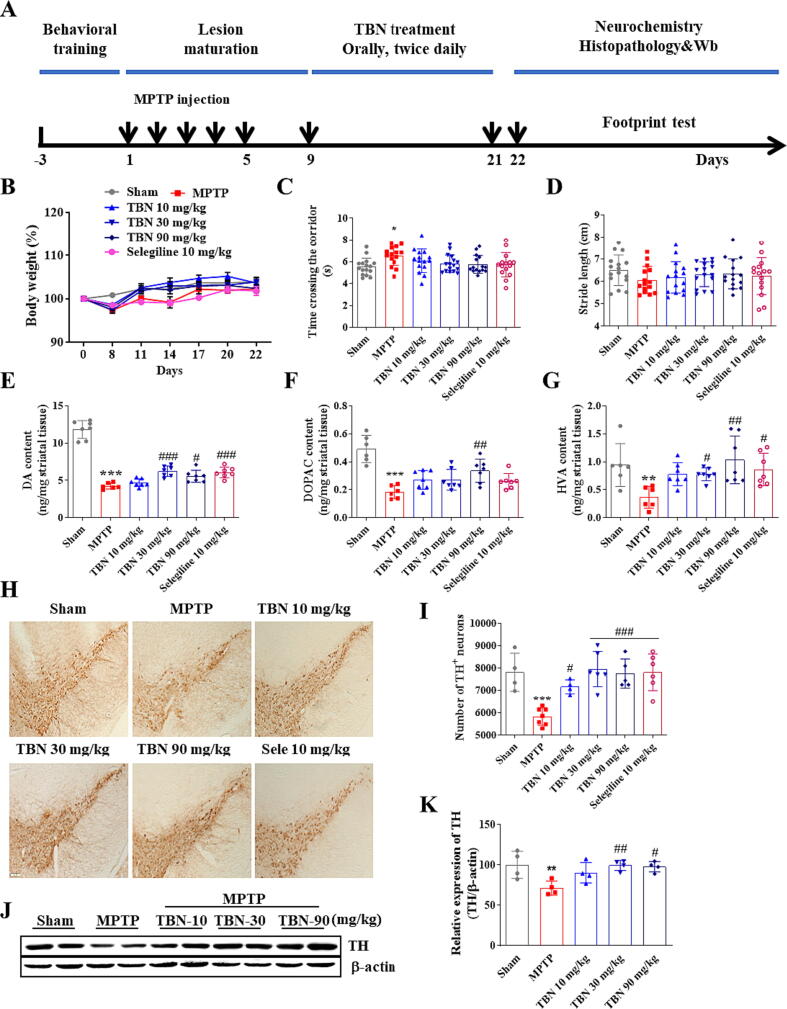
Fig. 4.
TBN improves motor behavior and protects SN neurons in the MPTP-induced mice PD model. (A) Experimental schedule. (B) Body weight (%). Data are mean ± SD of 15 or 16 mice per group. Data were analyzed using two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. (C) Time taken to cross the corridor (s). Data are mean ± SD of 15 or 16 mice per group. Data were analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. (D) Stride length (cm) in the footprint test. Data are mean ± SD of 15 or 16 mice per group. Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA and Dunnett’s multiple comparison tests. (E-G) Quantification of striatal DA, DOPAC, and HVA by HPLC. Data are mean ± SD of 6 or 7 mice per group. Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test (E, F) or Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons test (G). (H) Representative photomicrographs of immunohistochemistry staining for TH in the SN of MPTP mice. Scale bars, 100 μm. (I) Stereological counting of TH-positive neurons from SN. (J, K) Western blot for TH expression in the SN of MPTP mice. Data are mean ± SD of 4–7 mice per group. Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA and Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test (I-K). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 versus sham group; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 and ###P < 0.001 versus MPTP alone group.